
Tomo: Digital + Physical Medication Adherence Solution
Product Strategy & Business Impact
Tomo represents a comprehensive digital and physical solution addressing medication non-adherence, a healthcare crisis affecting over 131 million Americans and costing the industry $100+ billion annually. This project, sponsored by Cognizant, challenged us to design an integrated system that transforms how patients, caregivers, and healthcare providers approach medication management.
My Role: Lead UX Designer collaborating with one teammate over 3.5 months, handling end-to-end product design from generative research through user testing and visual design.
The Challenge: While 30-50% of prescribed medications aren’t taken as directed, leading to 700,000+ annual deaths, most non-adherence is unintentional. Patients want to comply but struggle with busy schedules, complex regimens, and lack of systematic support.
Market Research & Problem Validation
Understanding the Healthcare Crisis
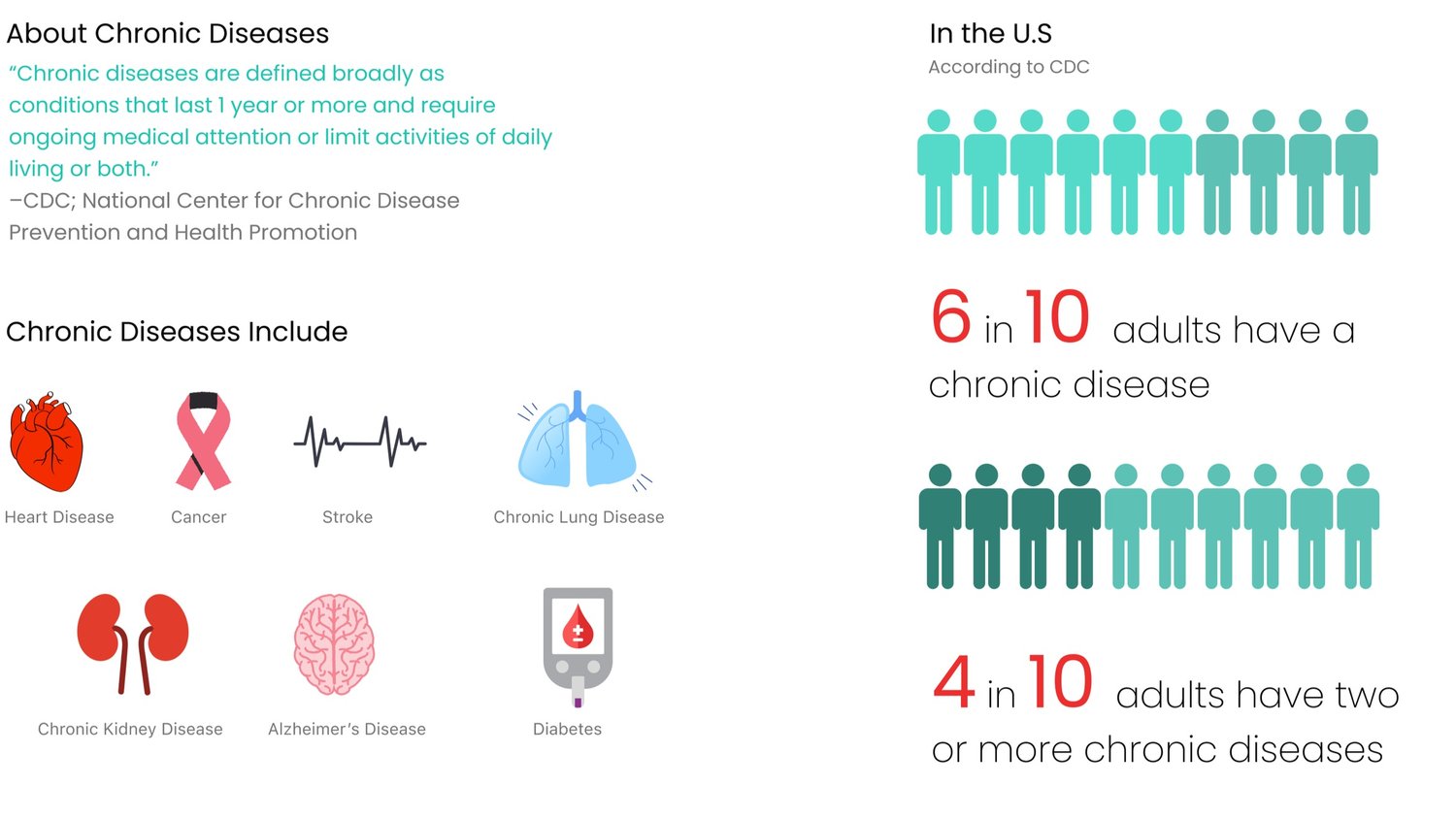
Our research revealed staggering market dynamics driving the need for innovative adherence solutions. To understand the current percentage of adults and older millennials in the United States with chronic medical conditions, we conducted comprehensive secondary research analyzing 4,012 respondents across all age groups.
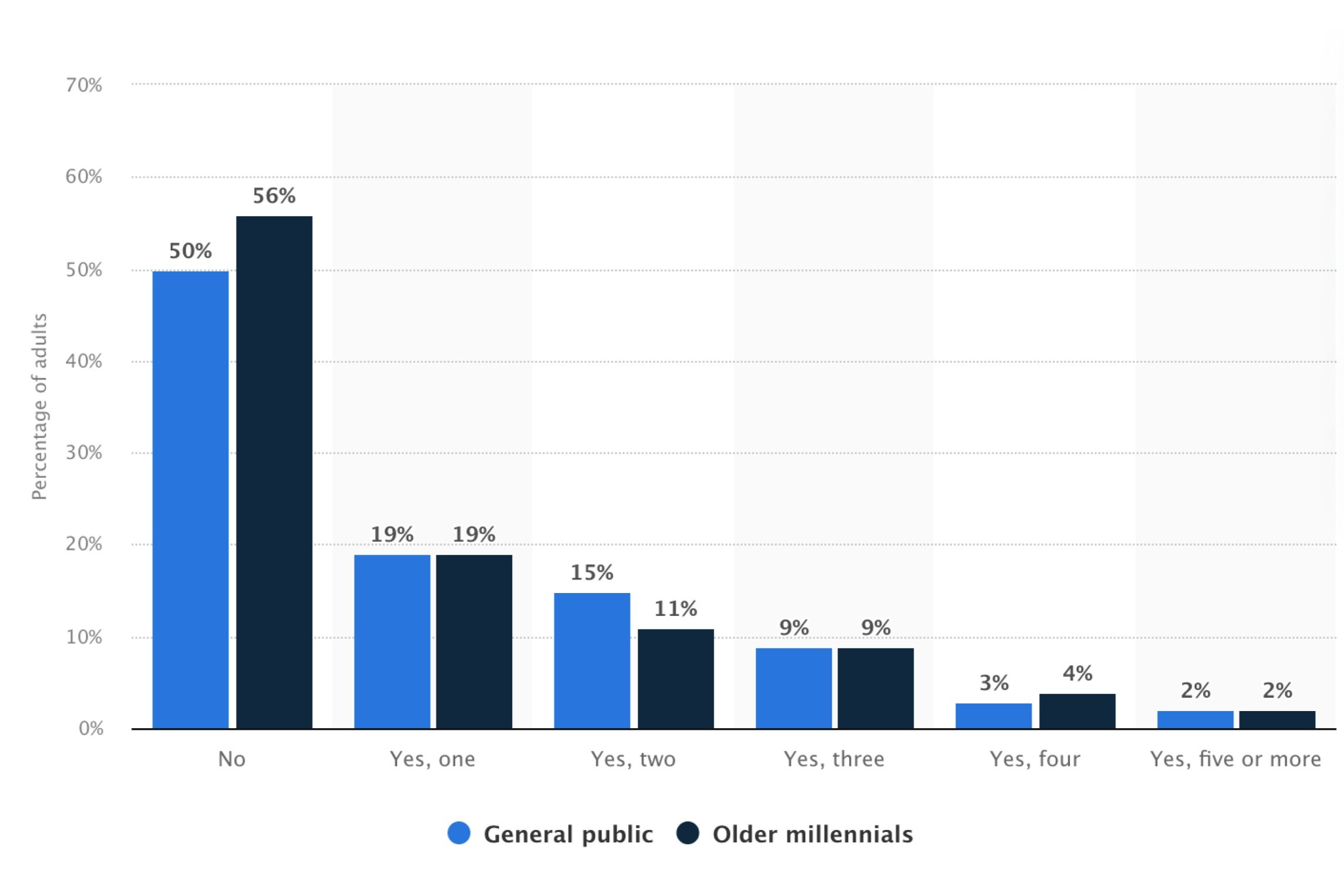
The demographic data revealed that chronic disease management increasingly affects younger populations, with millennials showing concerning rates of multiple chronic conditions. This insight shifted our design strategy toward solutions that could serve both traditional elderly populations and younger, more technology-savvy users.
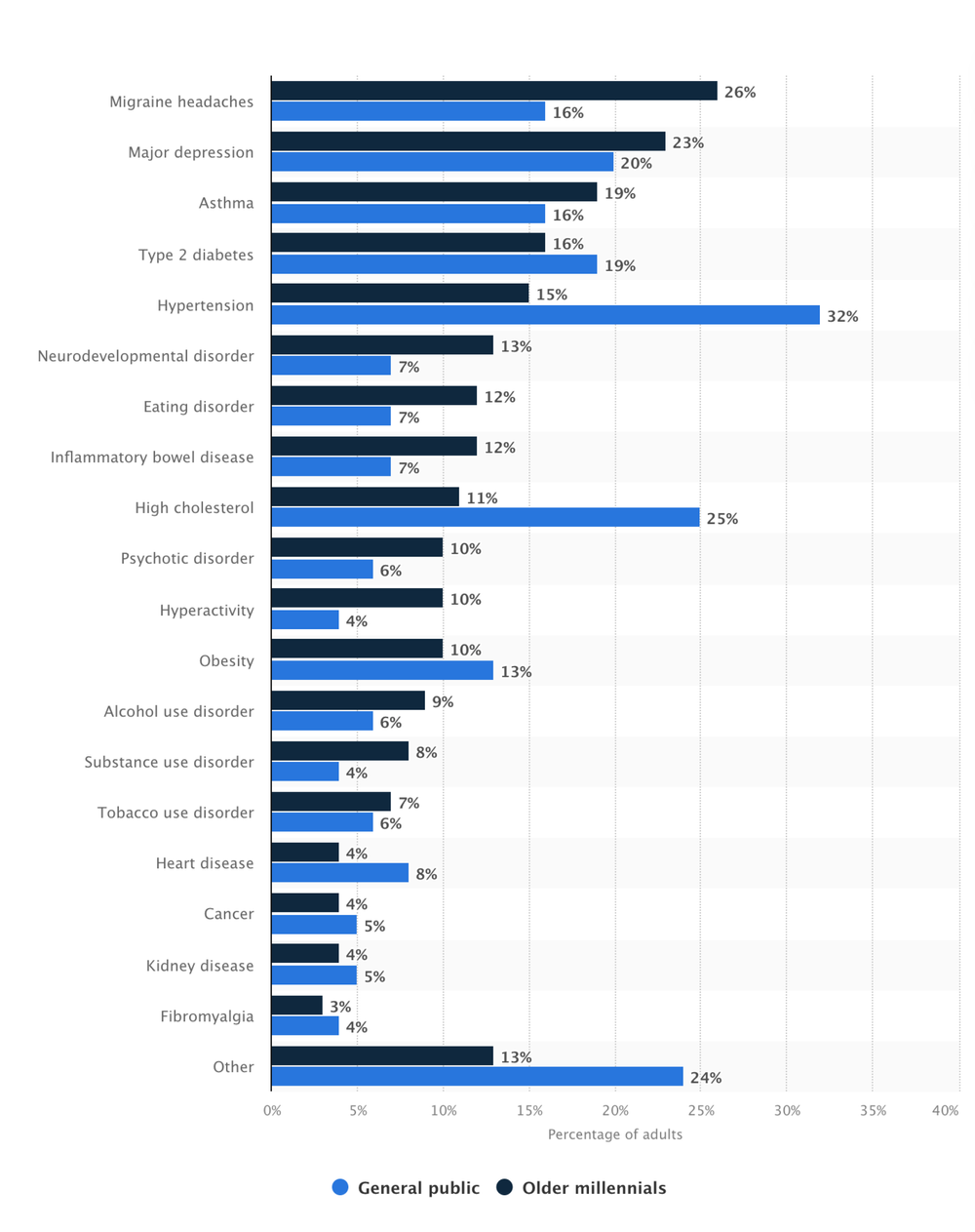
Going further in depth, we investigated how chronic diseases affected an aging population to understand the full scope of our addressable market.
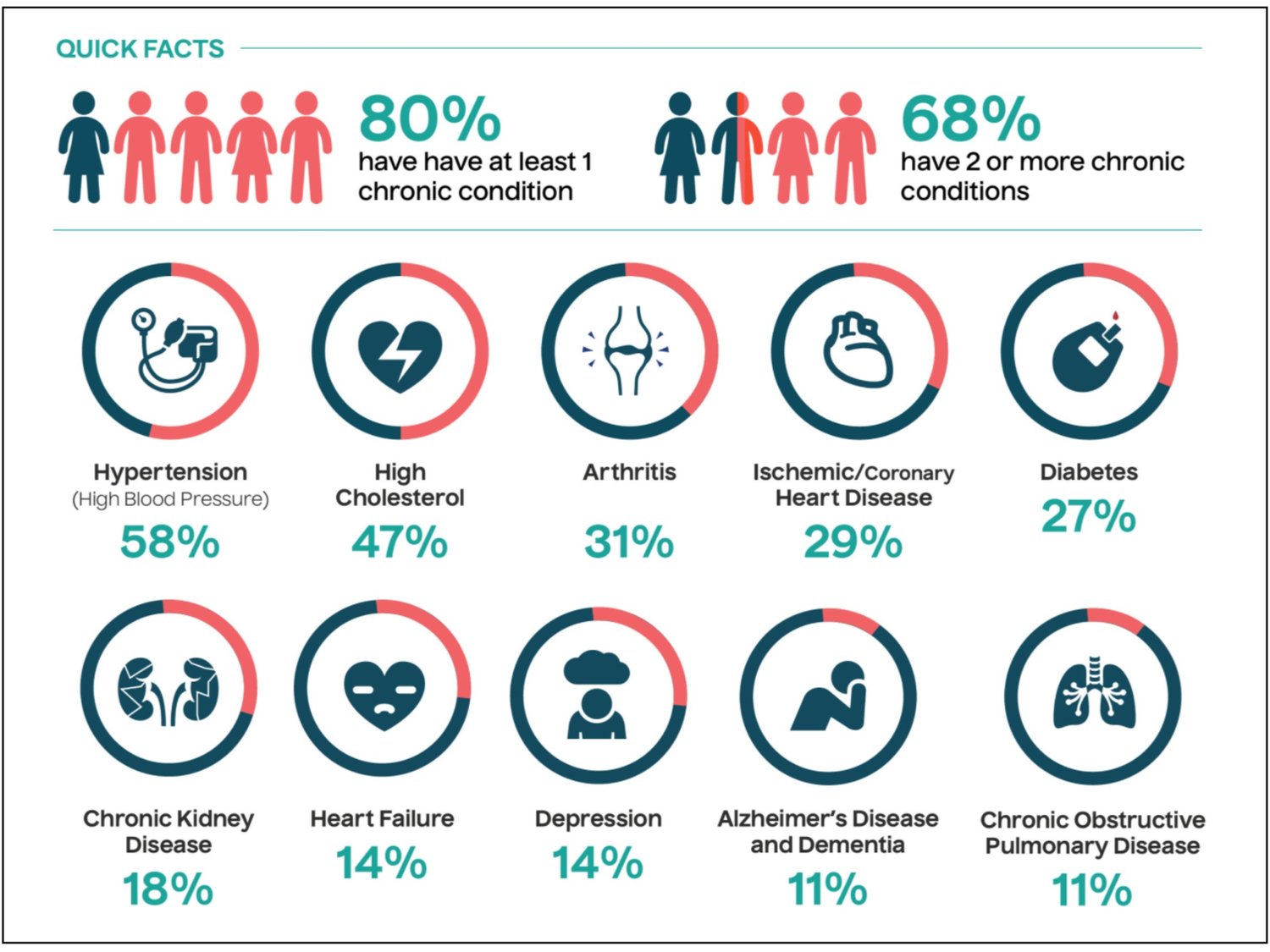
Our research highlighted critical market realities: over 157 million Americans are expected to live with chronic diseases by 2023, with healthcare costs projected to exceed $4.2 trillion. Patients with chronic illness utilize hospitals and emergency rooms at higher rates than the general population, putting further strain on the healthcare system.
Prescription Drug Usage Patterns
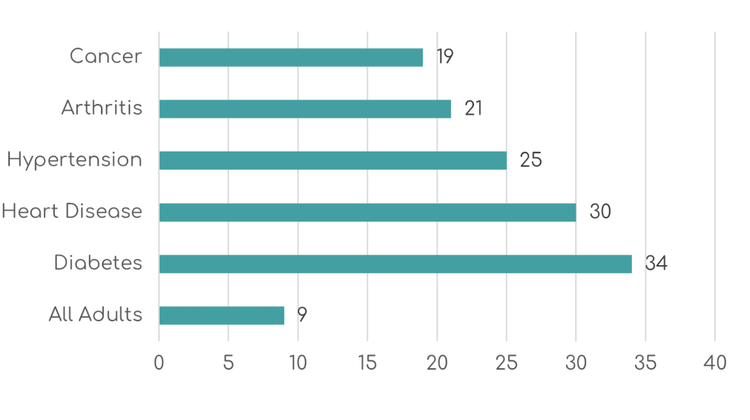
Research from Georgetown University’s Health Policy Institute showed that 66% of US adults—over 131 million people—take prescription drugs. Among patients with chronic conditions like diabetes, arthritis, and heart disease, prescription drug usage reaches 89-98%. These numbers validated the massive addressable market for adherence solutions.
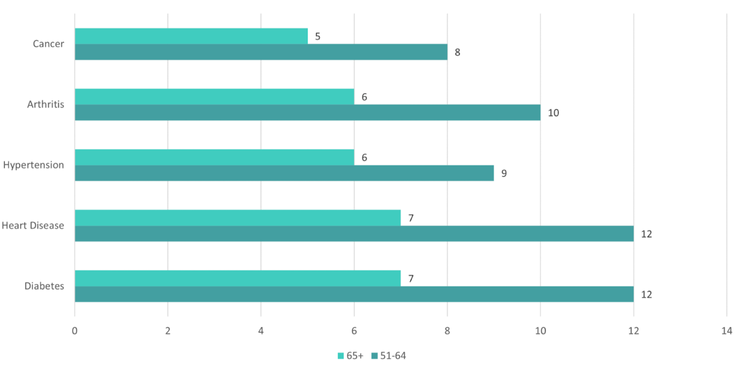
Prescription usage patterns revealed increasing complexity with age, from 18% of children under 12 to 85% of adults over 60. This demographic progression informed our dual-approach strategy: designing for both independent younger users and caregiver-supported older populations.
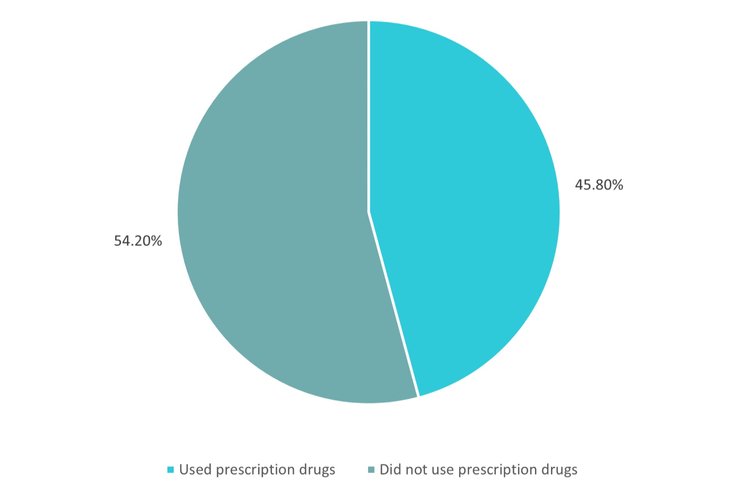
Understanding Non-Adherence Causes

Our analysis revealed that non-adherence stems from complex user-centered factors requiring different design approaches. Rather than treating this as a purely medical problem, we recognized it as a behavioral design challenge with multiple interconnected causes.
Unintentional Non-Adherence Factors

The majority of non-adherence stems from practical challenges rather than intentional resistance. Patients forget medications due to busy schedules, irregular routines, or cognitive limitations. This insight became crucial for our design approach—the solution needed to integrate seamlessly into existing daily patterns.

Complex medication schedules particularly challenge patients with multiple chronic conditions. Taking medications incorrectly or at wrong times can cause adverse reactions, creating a cycle where poor adherence leads to worse health outcomes and even more complex treatment requirements.
Intentional Non-Adherence Patterns

Personal beliefs and perceptions may conflict with prescribed regimens, influenced by social stigma around illness and medication or pressure from family and friends. Understanding these emotional factors informed our approach to discrete, non-medical aesthetics.
Intentional nonadherence often depends on cognitive assessment and rational decision-making about treatment benefits. Trust in physicians, acceptance of diagnosis, and belief in provider intentions all factor into patient adherence decisions.

Patients frequently make calculated decisions about medication, weighing perceived side effects against benefits or questioning necessity when symptoms aren’t severe. This behavior pattern required our solution to include educational components and transparent communication channels.

Lack of knowledge about diagnosis and treatment necessity often drives intentional non-adherence. Many medications require specific circumstances for effectiveness—timing, food interactions, or administration methods—highlighting the need for educational integration within our design.
Healthcare System Impact

The World Health Organization identified medication non-adherence as a primary cause of healthcare morbidity, mortality, and cost increases. Beyond individual health outcomes, poor adherence contributes to antimicrobial resistance, with 700,000 deaths annually attributed to resistant organisms—often resulting from incomplete antibiotic regimens.
Competitive Landscape Analysis

We conducted comprehensive competitive analysis to understand existing solutions and identify market gaps. This research helped us assess which demographic groups were being targeted and how effectively current solutions addressed the broad spectrum of non-adherence causes.
Market Analysis: Karie

Karie offers a device plus companion app model with one-time product costs plus monthly subscription fees. The system manages and delivers medication while coordinating with personal and medication schedules through visual and auditory reminders. Caregivers can receive nonadherence notifications, but the solution lacks portability for active lifestyles.
Market Analysis: Hero

Hero requires $299.88 annual or $29.99 monthly subscription fees for their device plus companion app system. While offering remote caregiver monitoring and automatic refills with free delivery, the high cost and home-based design miss younger, mobile demographics.
Our competitive analysis revealed significant gaps in existing solutions. Most products targeted either digital-only approaches with high abandonment rates or expensive home-based systems that lacked portability and served narrow demographics.
Strategic Design Challenge
Based on our research findings, we identified the core design challenge: How might we help users understand the importance of medication adherence while providing caregivers and physicians effective monitoring tools, keeping users motivated and tracking their adherence journey?
Our design objective became developing and testing synergistic physical and digital solutions that could monitor and ensure patients follow prescribed medication regimens while addressing the complex behavioral, educational, and systematic challenges we’d identified.
Design Concerns
Throughout our design process, we needed to address several critical concerns that could impact user adoption and effectiveness:
- Patient beliefs
- Patient preferences
- Barriers to medication-taking: cost, technological access and abilities, concerns about treatment and use
- Patients have complex, difficult-to-follow regimens
- Patients don’t understand the reasons for treatment or believe side effects outweigh the benefits
- Patients may take medication on time in the beginning but don’t think it is effective and stop taking it
- Language barriers
- Disconnect between provider and patients; for example, getting generic medicines with different formulas instead of the prescribed medicine
- Social pressure from friends
- Religious pressure
- Patients want to take medication on time but always forget
User Research & Primary Insights
Survey Research Findings
We disseminated online surveys to learn about user demographics, habits, and needs, receiving responses from 61 participants across diverse socioeconomic backgrounds and age ranges.
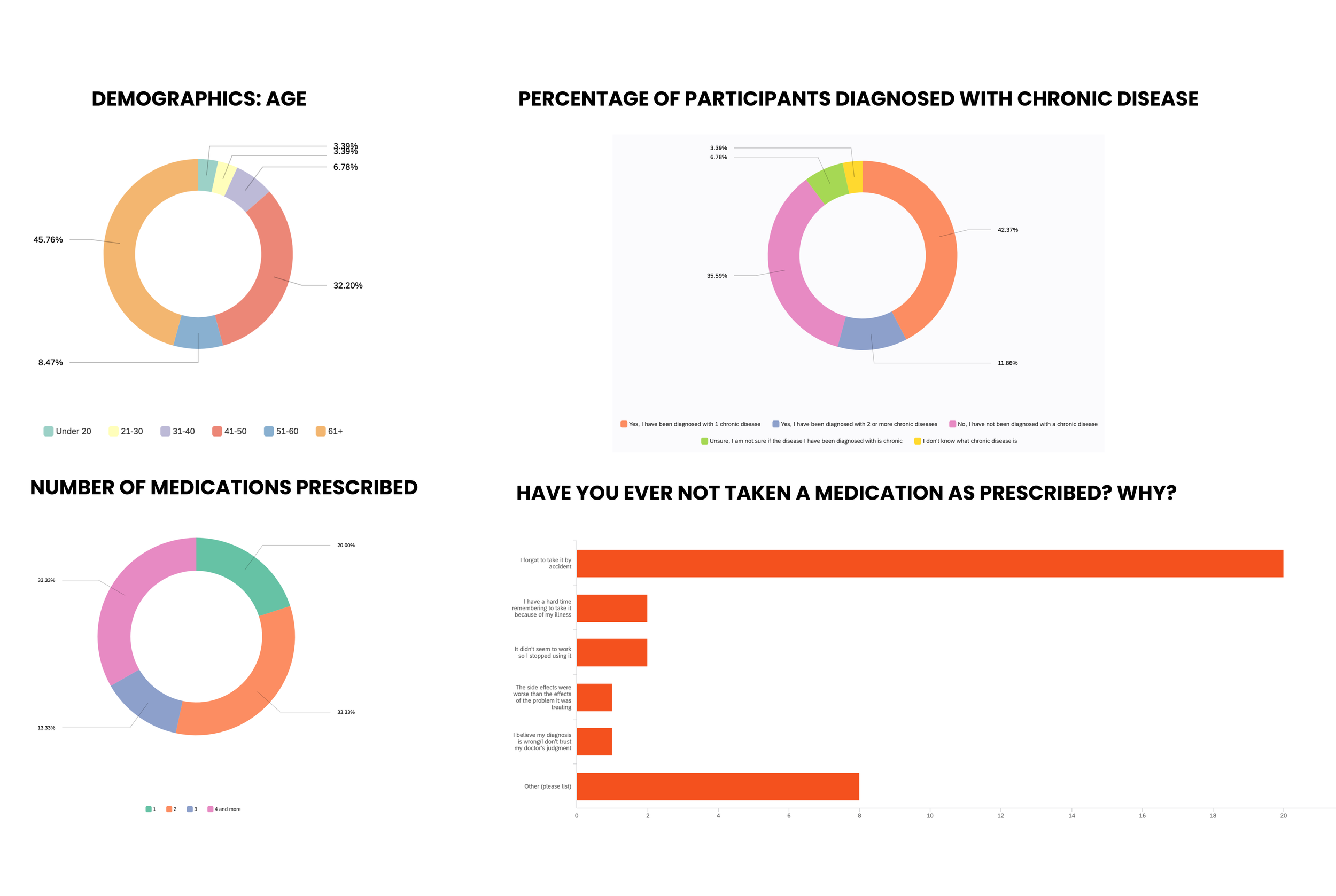
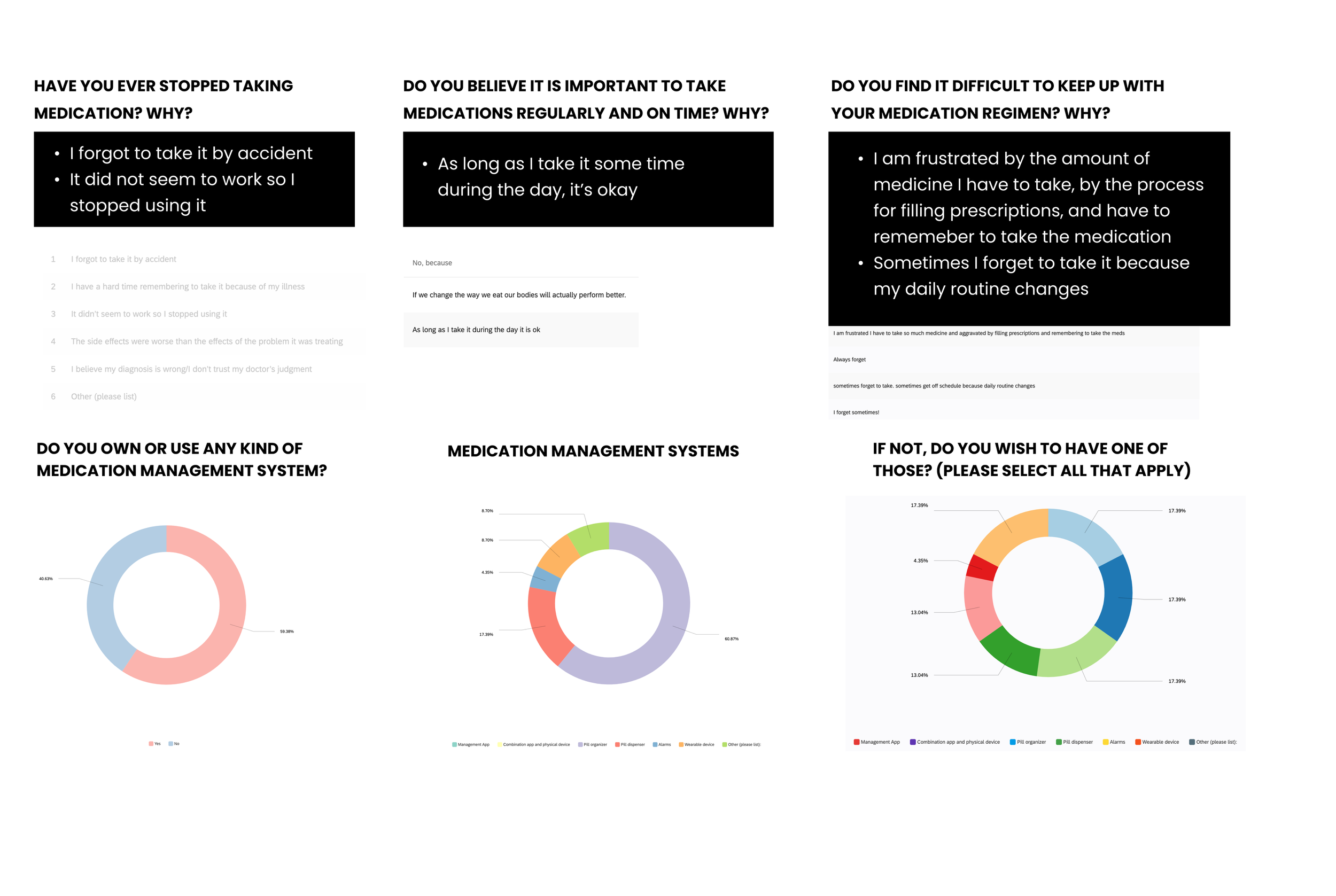
The survey questions helped us understand why participants weren’t taking medications as prescribed and whether they used any medication management systems to assist with adherence.
User Interview Insights
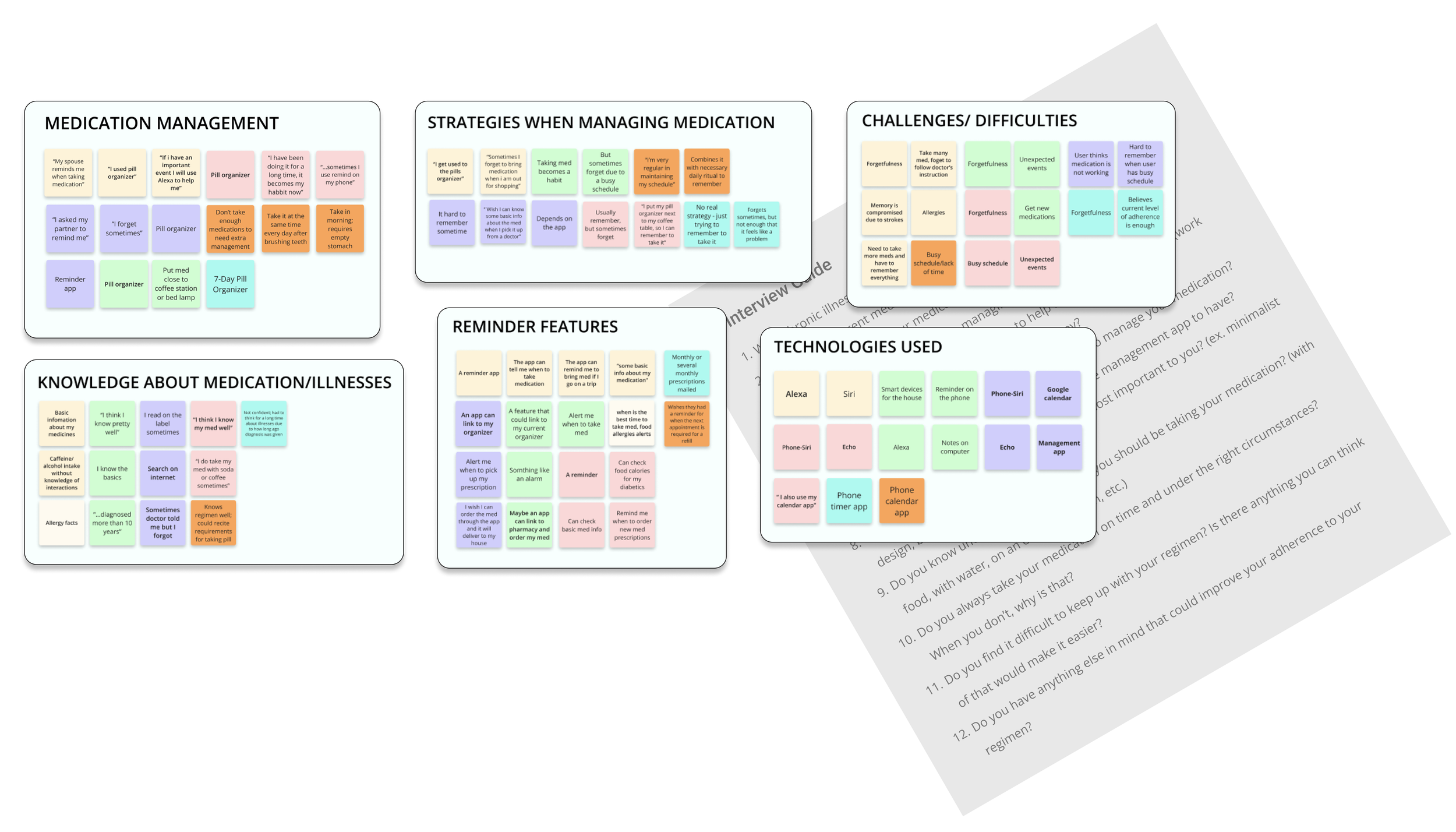
We conducted user interviews with seven chronically ill prescription medication users to gain deeper understanding of pain points in maintaining consistent regimens, medication management styles, technology usage, and participants’ knowledge about adherence importance.
Themes
Participants think they know their regimens well and do not seem to understand the importance of adherence. Many started taking medications with alcohol or caffeinated beverages.
Participants are confident with their medication management because they have been using them for a long time but still need help with a reminder system.
Pain Points
- Users want to take medication on time but always forget
- Users think they know their medication and regimen well because they have been taking said medication for a long time
- Users do not think nonadherence is a major problem
- Users discover that picking up and dropping off prescriptions is time consuming and can find it difficult to find time to do so
- Users get frustrated at the lack of communication between the physician and the pharmacist, which can cause missed doses while waiting for an appointment
Opportunities
- Reminders pads
- Physical device linked with an app
- Appointment reminders
- Refill reminders
- Cross-communication between physicians & pharmacists
- Education
User Personas & Strategic Insights
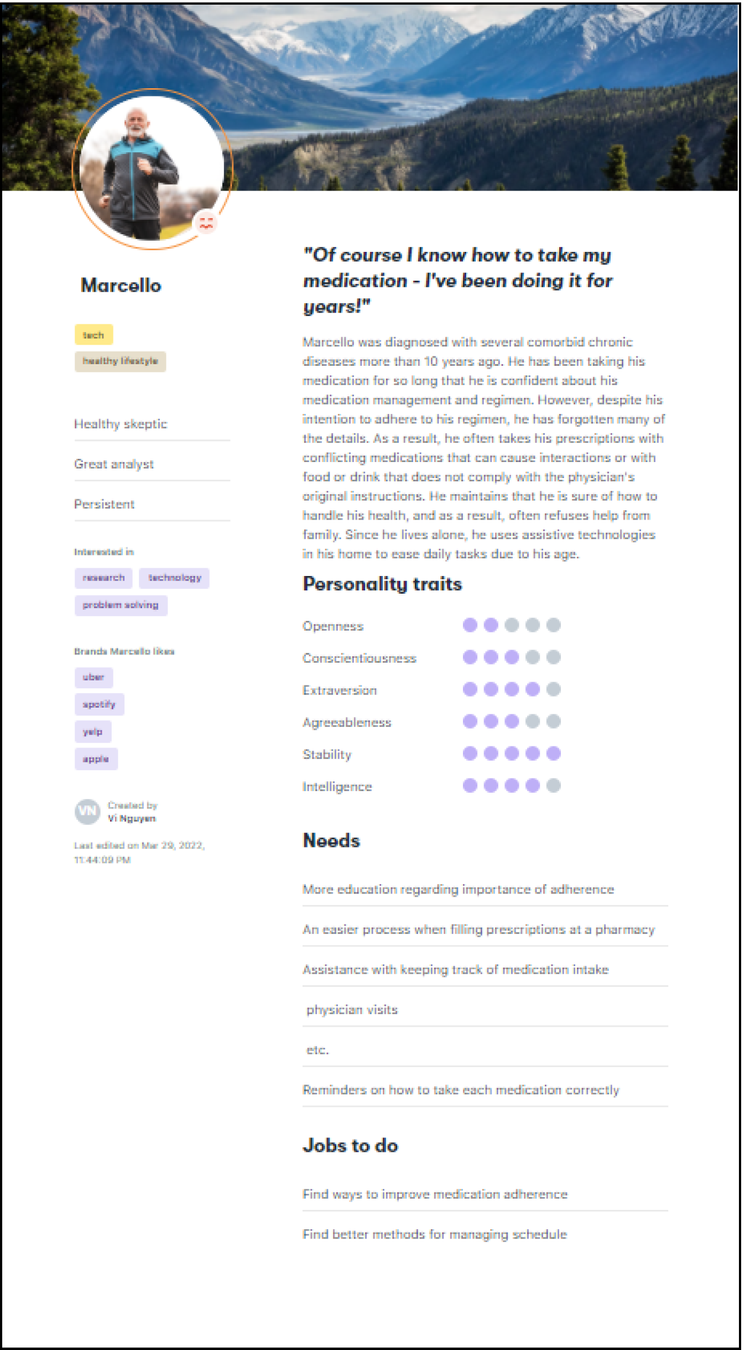
Marcello represents the overconfident manager - a long-time chronic illness sufferer who believes he’s adherent but has forgotten original physician directions. His resistance to change and belief in his current approach required subtle, supportive design interventions rather than corrective messaging.
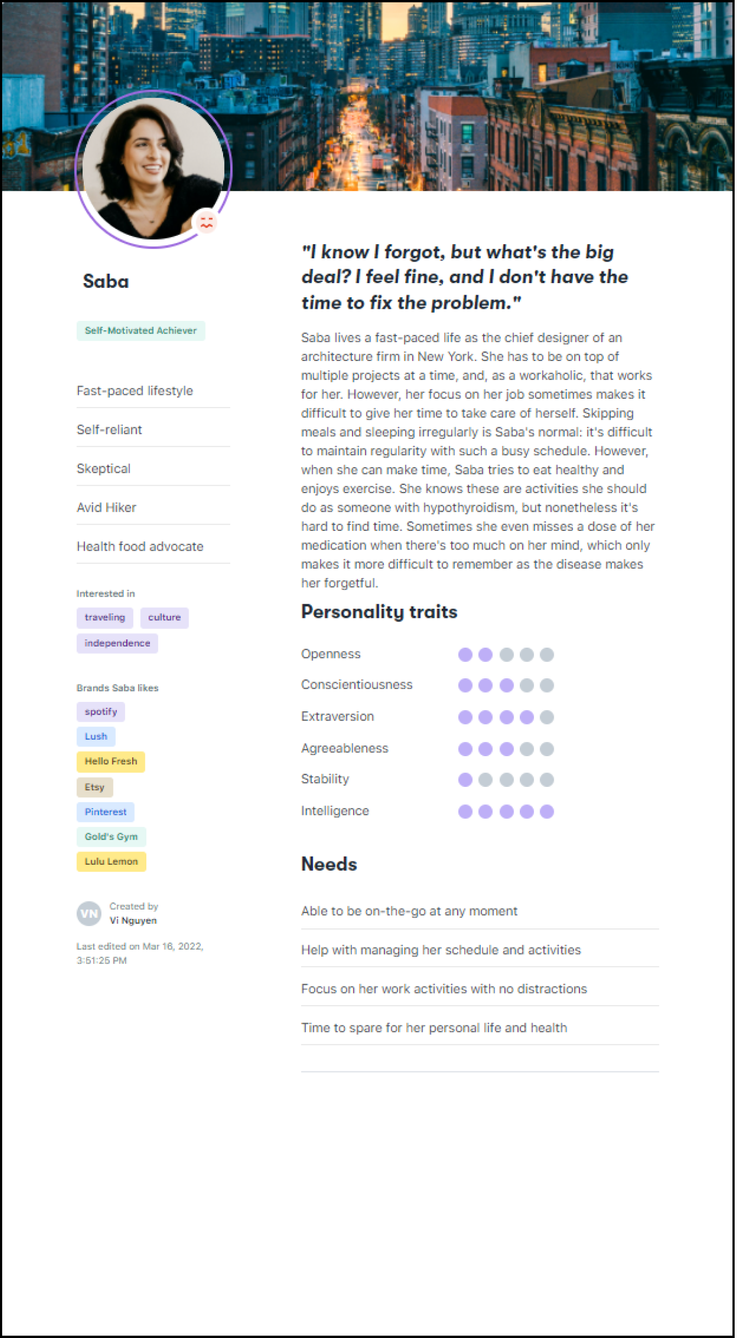
Saba embodies the busy professional - whose non-adherence stems from scheduling challenges. While acknowledging her struggles, she doesn’t see immediate health impacts, making her receptive to convenient solutions but requiring evidence of benefit to drive adoption.
These personas drove our design toward flexible, adaptive interfaces that could serve different levels of awareness and engagement without alienating users who felt confident in their current approaches.
Value Proposition & User Journey
“A synergistic digital application and physical product solution designed to assist those with chronic illnesses adhere to their medication regimen appropriately without overcomplicating their routines.”
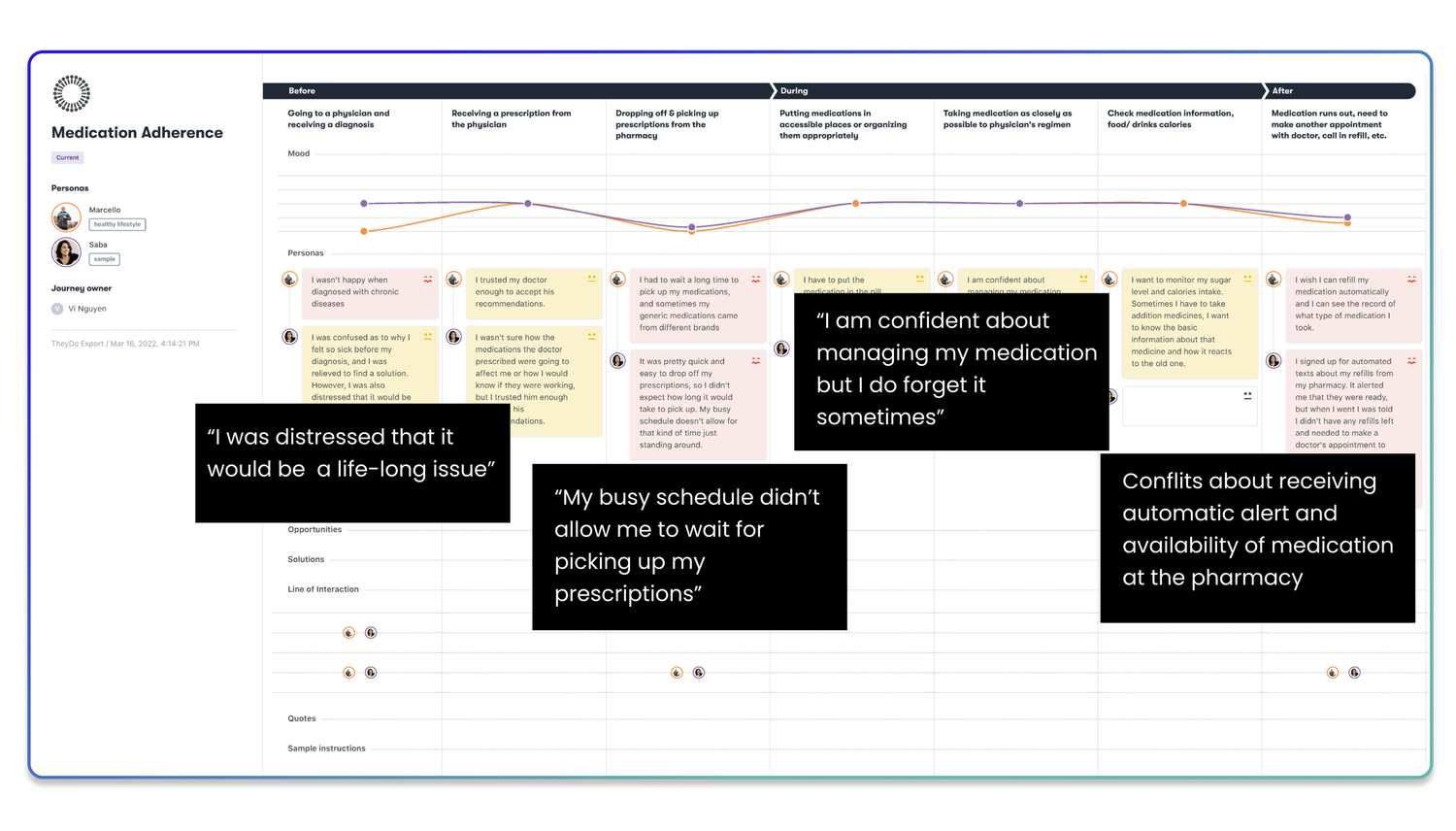
We analyzed the current user journey from diagnosis through regular medication management, identifying seven critical steps: receiving diagnosis, getting prescriptions, pharmacy interactions, medication storage, taking medications as prescribed, accessing medical data, and refill management.
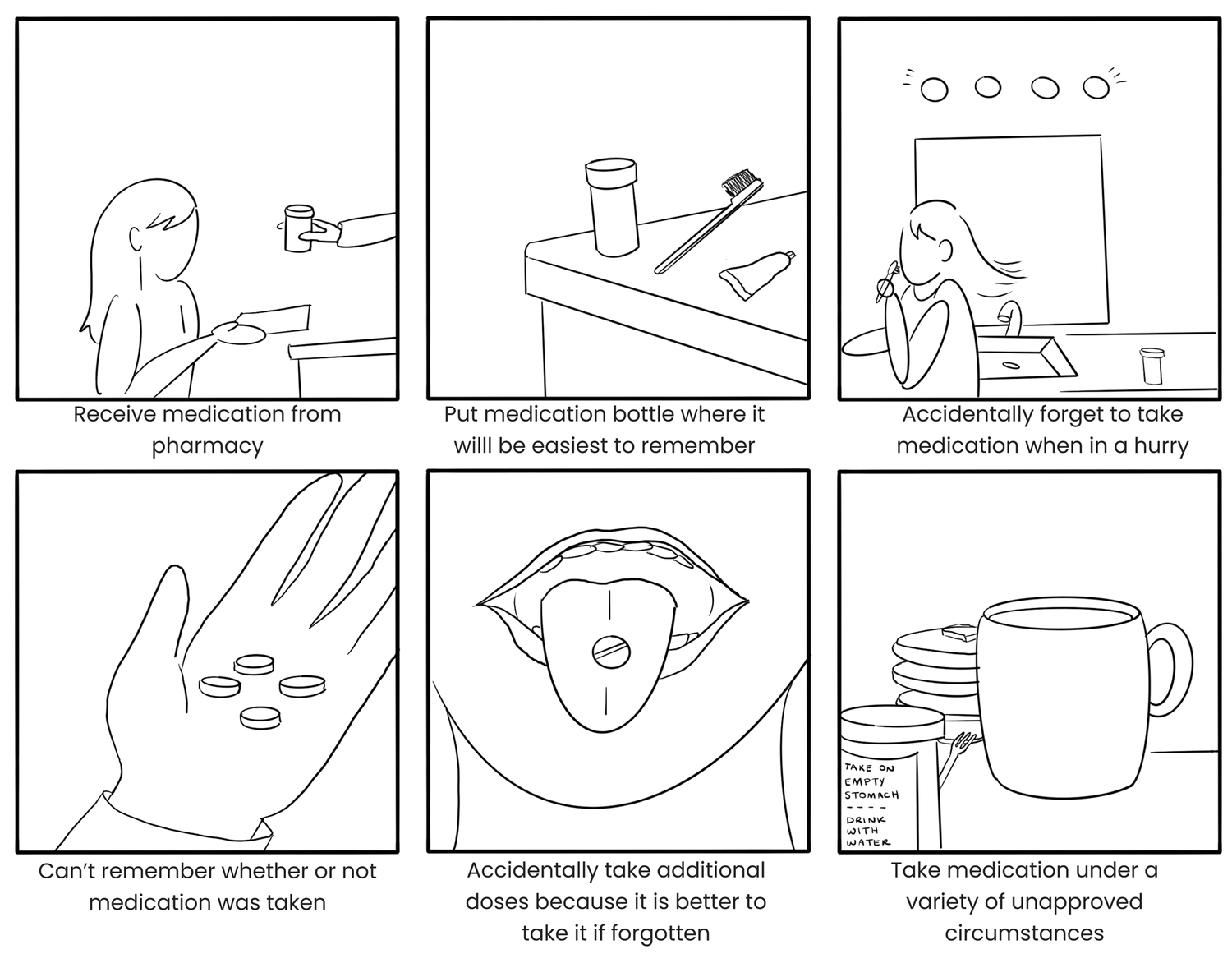
Our current state storyboard visualized consumer experiences from medication pickup through home usage, drawing directly from interviewee examples to understand real behavioral patterns and pain points.
Business Strategy & Ecosystem Design
Stakeholder Ecosystem
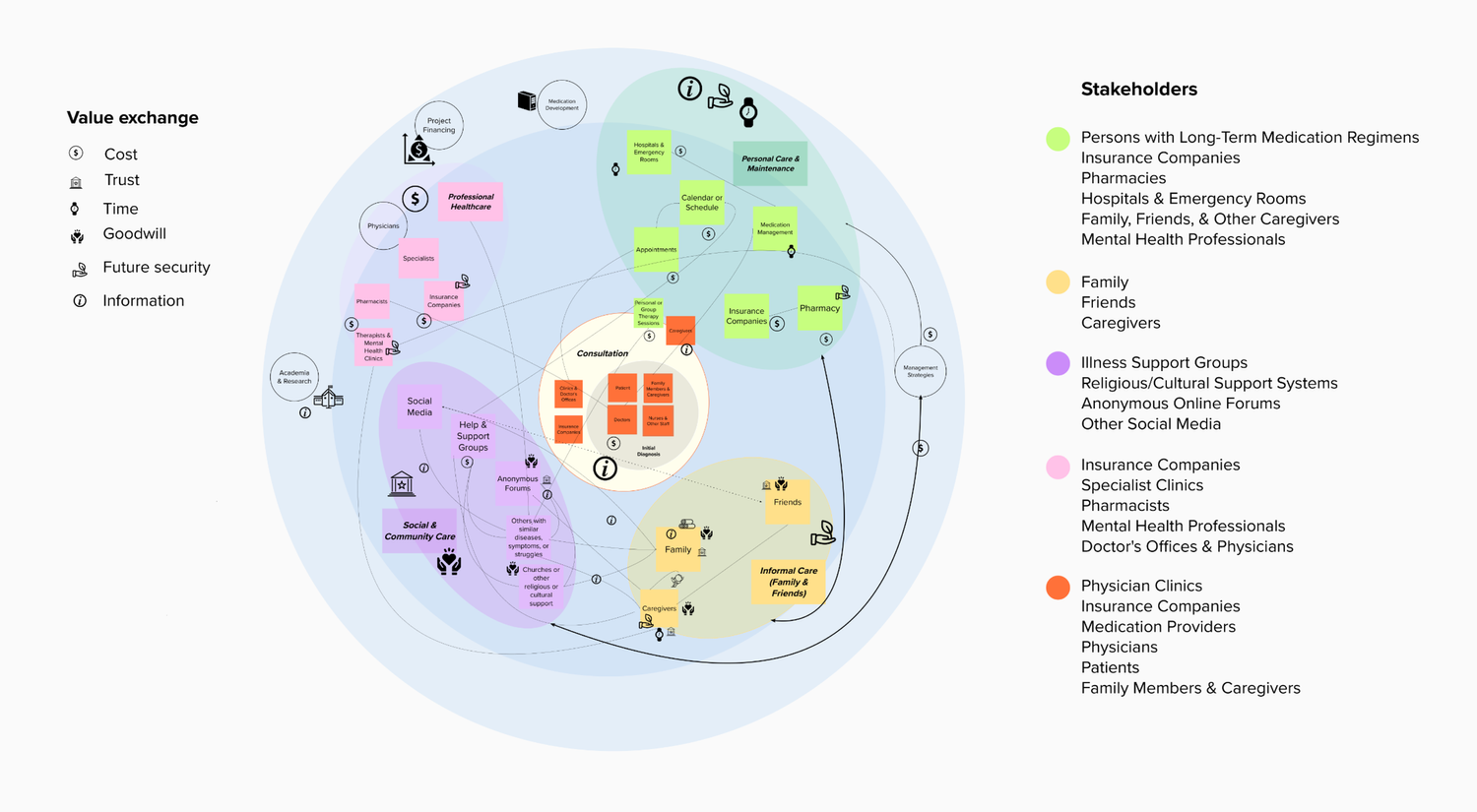
We designed an ecosystem map visualizing main stakeholders in patient medication adherence and identifying value exchanges between entities. The map covers initial consultation and diagnosis, personal care, informal and family care, social and community care, and professional care, with value exchanges including time, trust, money, information, goodwill, and security.
Business Model Strategy
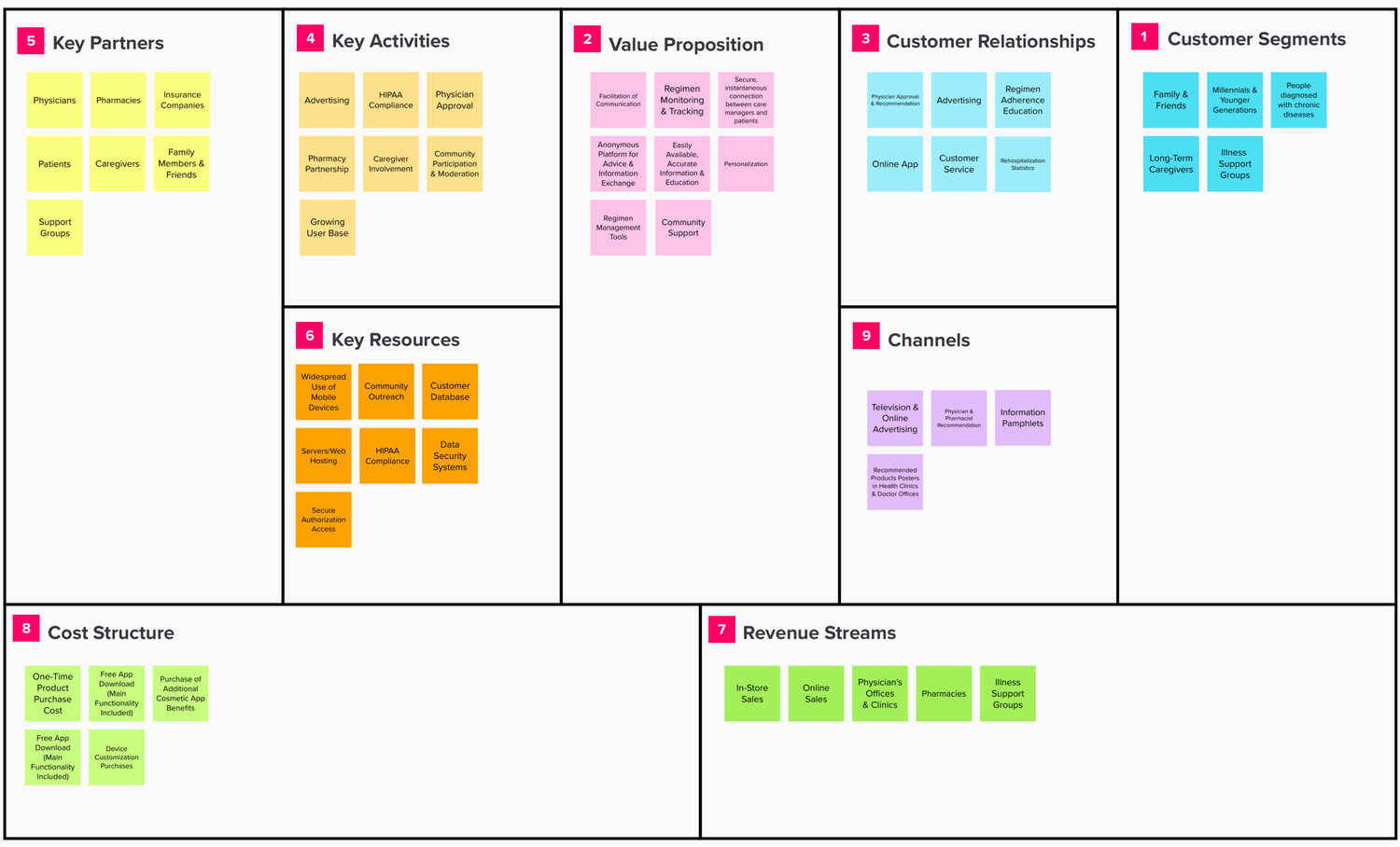
Our business model canvas outlines advantages, targets, risks, costs, and opportunities for the proposed solution. While the medication adherence solution could be sold as a standalone product, partnering with pharmacies and physicians to recommend and inform patients about the solution would benefit the entire ecosystem.
Design Process & Concept Development
Initial Ideation
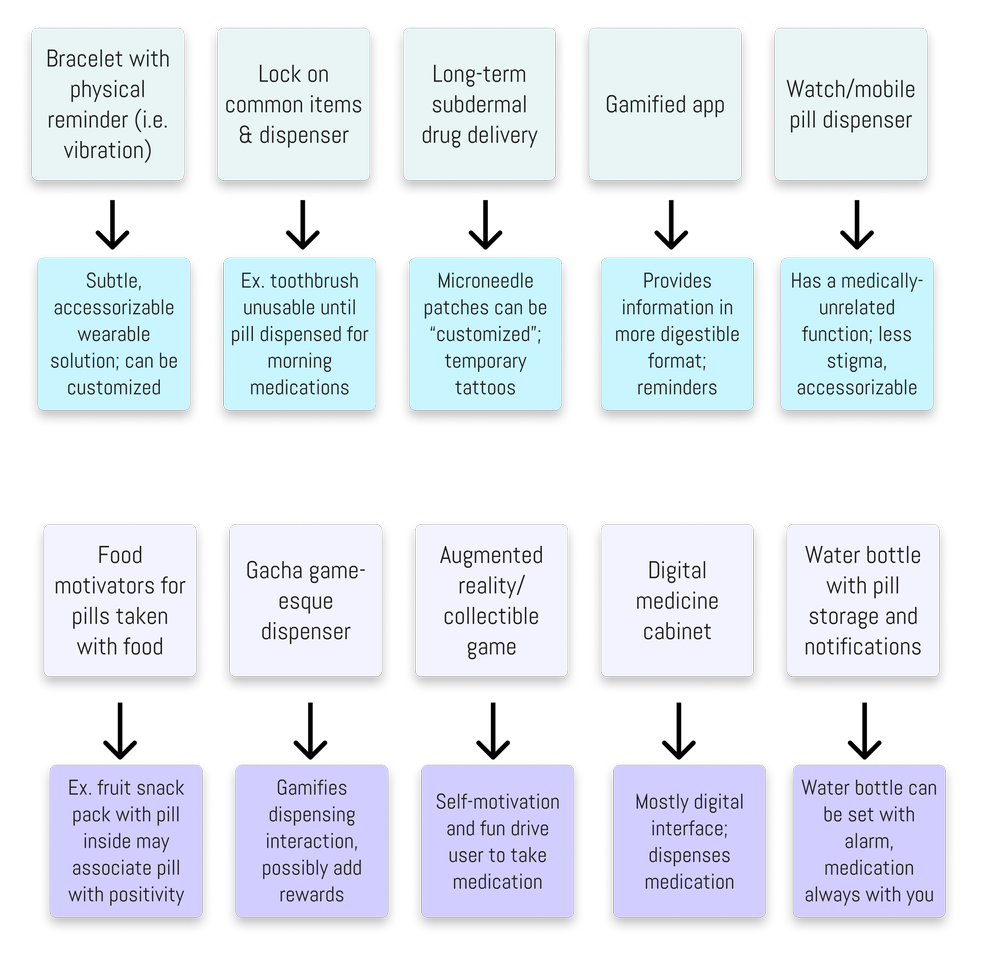
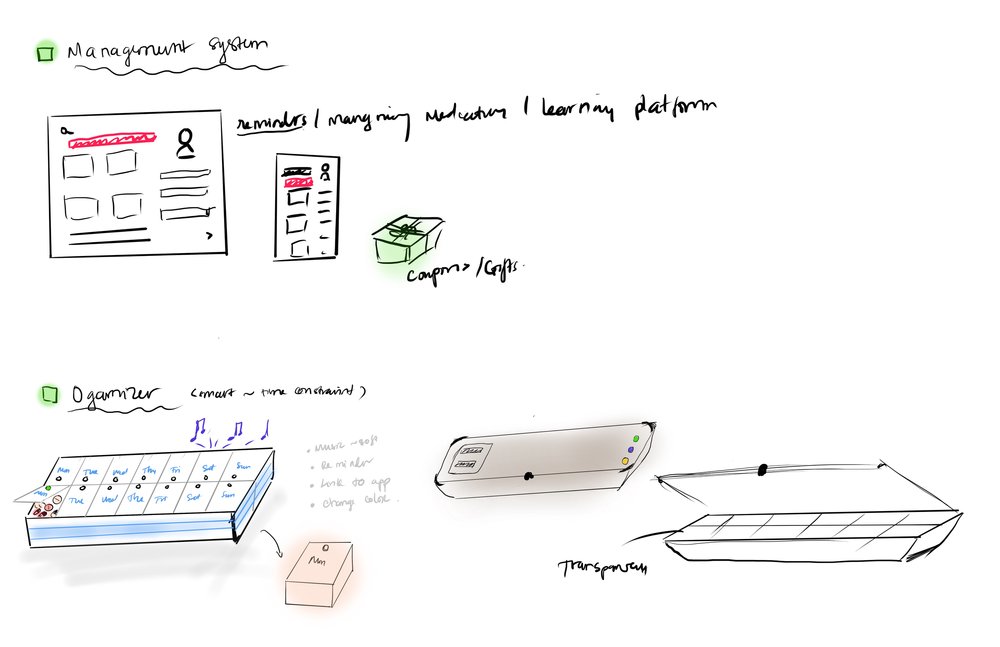
Initial ideation consisted of rapid brainstorming and preliminary concepts that we analyzed using an ideation matrix to identify key factors within each solution approach.
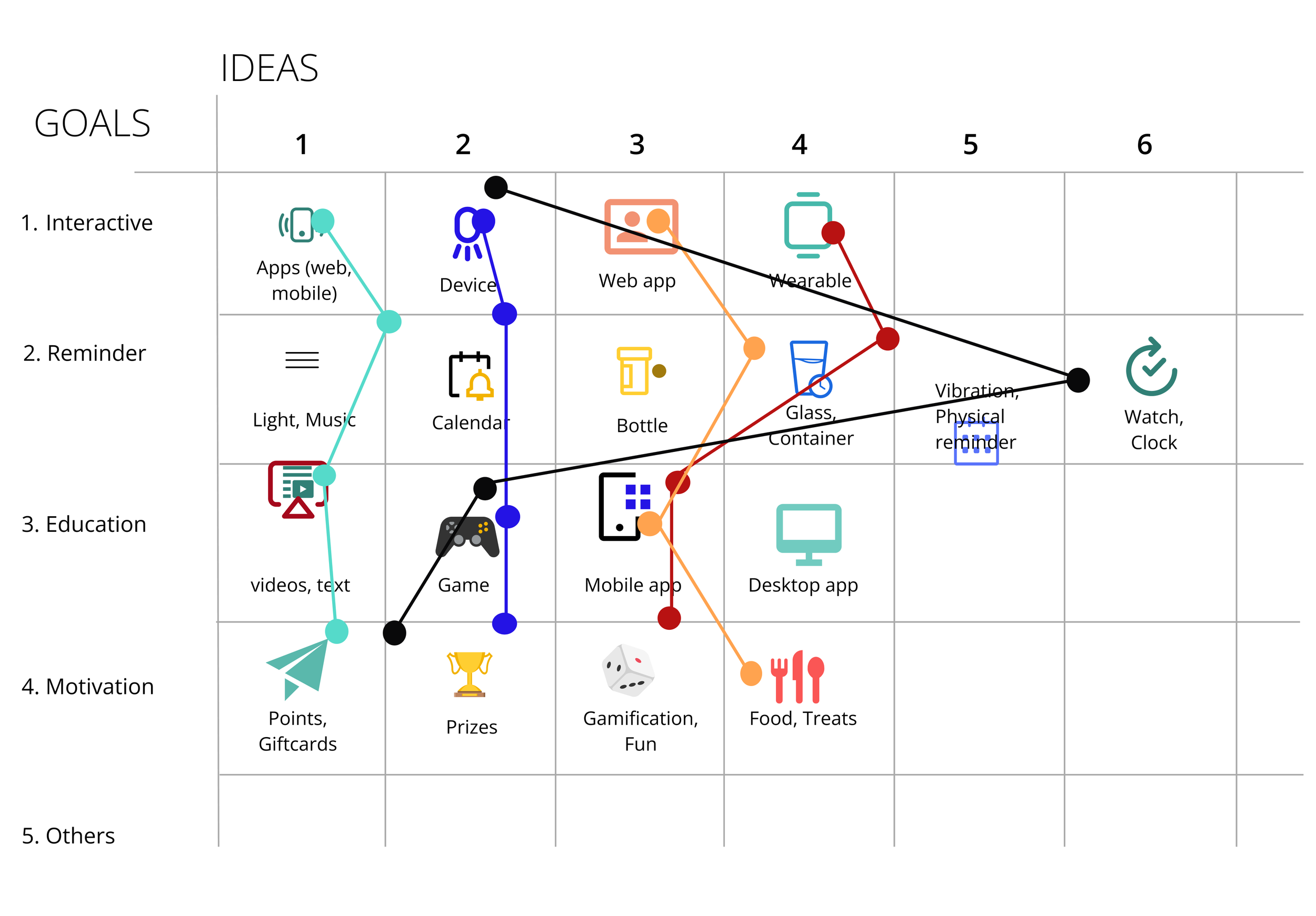
We used the ideation matrix to examine goals and ideas from our brainstorming sessions, identifying key factors that would contribute to the final concept. Each colored line represents factors within primary concept directions.
Physical Product Concepts
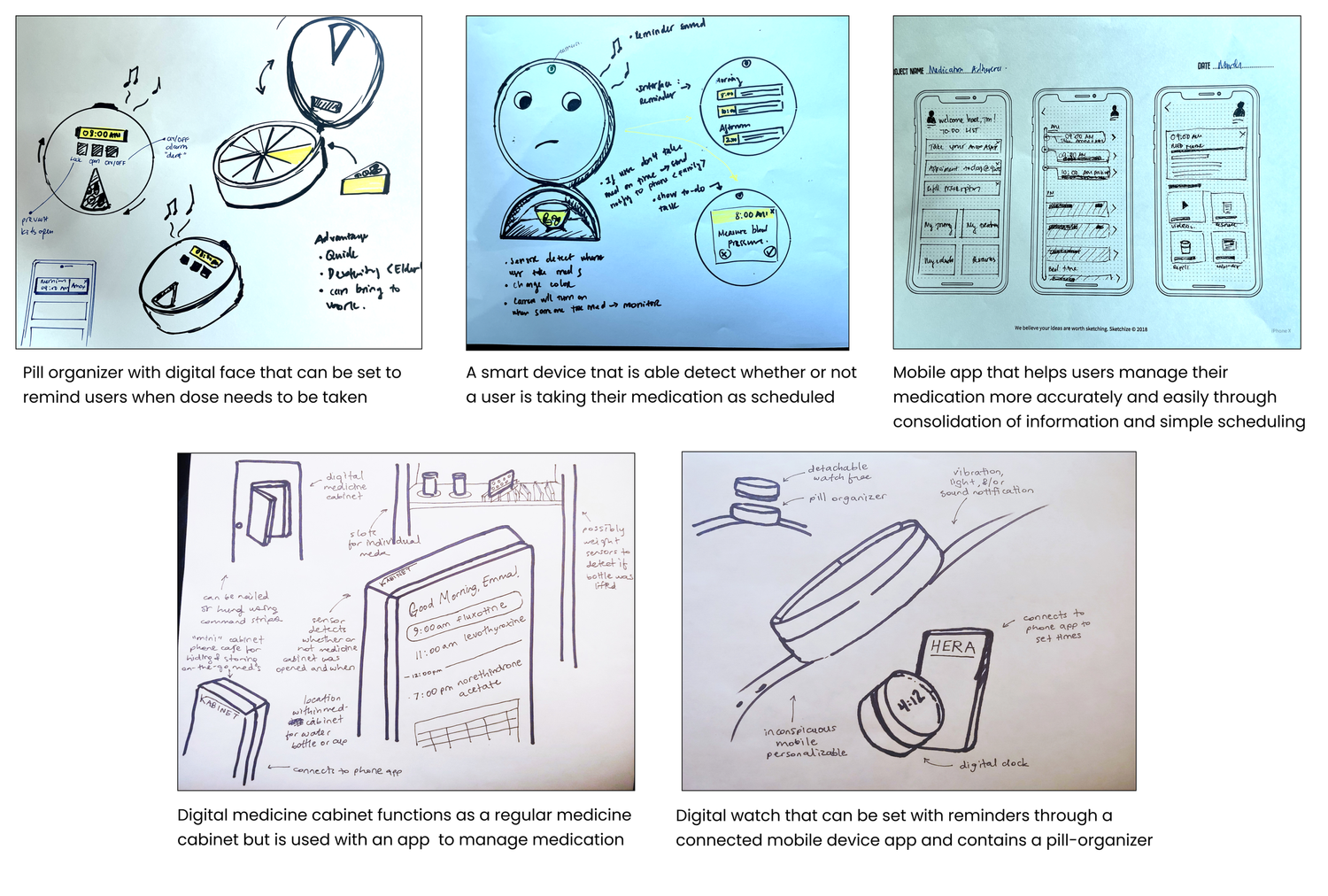
Our physical product concept integrated digital aspects with tangible reminder systems that alert users when it’s time for medication. The system incorporated gamification elements where users could earn points and rewards for adherence.
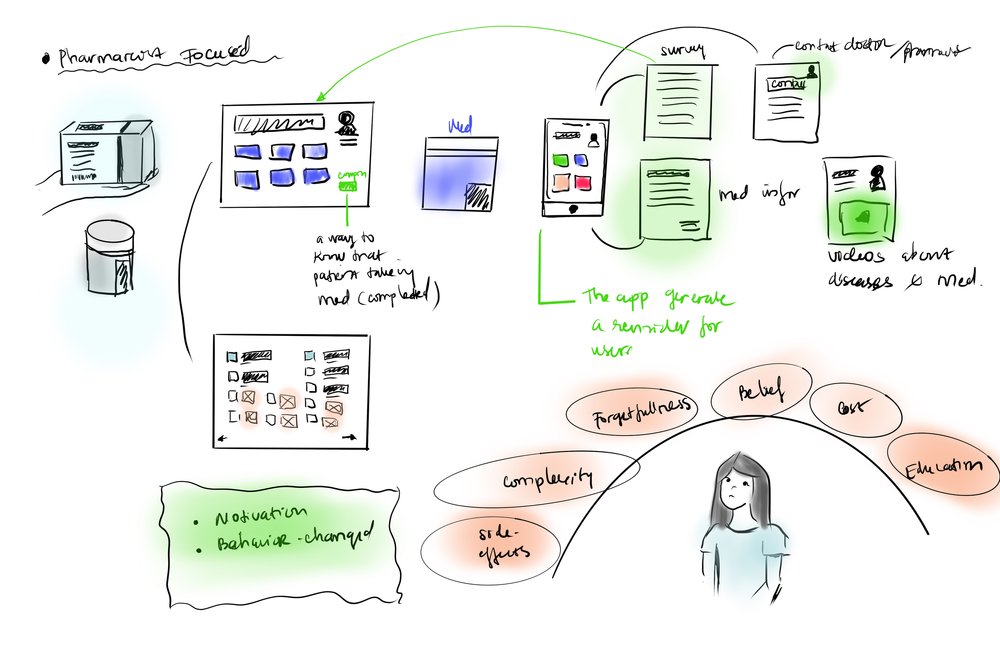
This concept focused on creating a management system connecting pharmacies, physicians, and end users for improved communication clarity. The system would work with physical models to provide medication reminders.
This ecosystem concept emphasized the pharmacy’s role within the adherence system, aiming to motivate and change user behavior through a mobile application that generates reminders for appointments, refills, and dose times while providing educational resources.
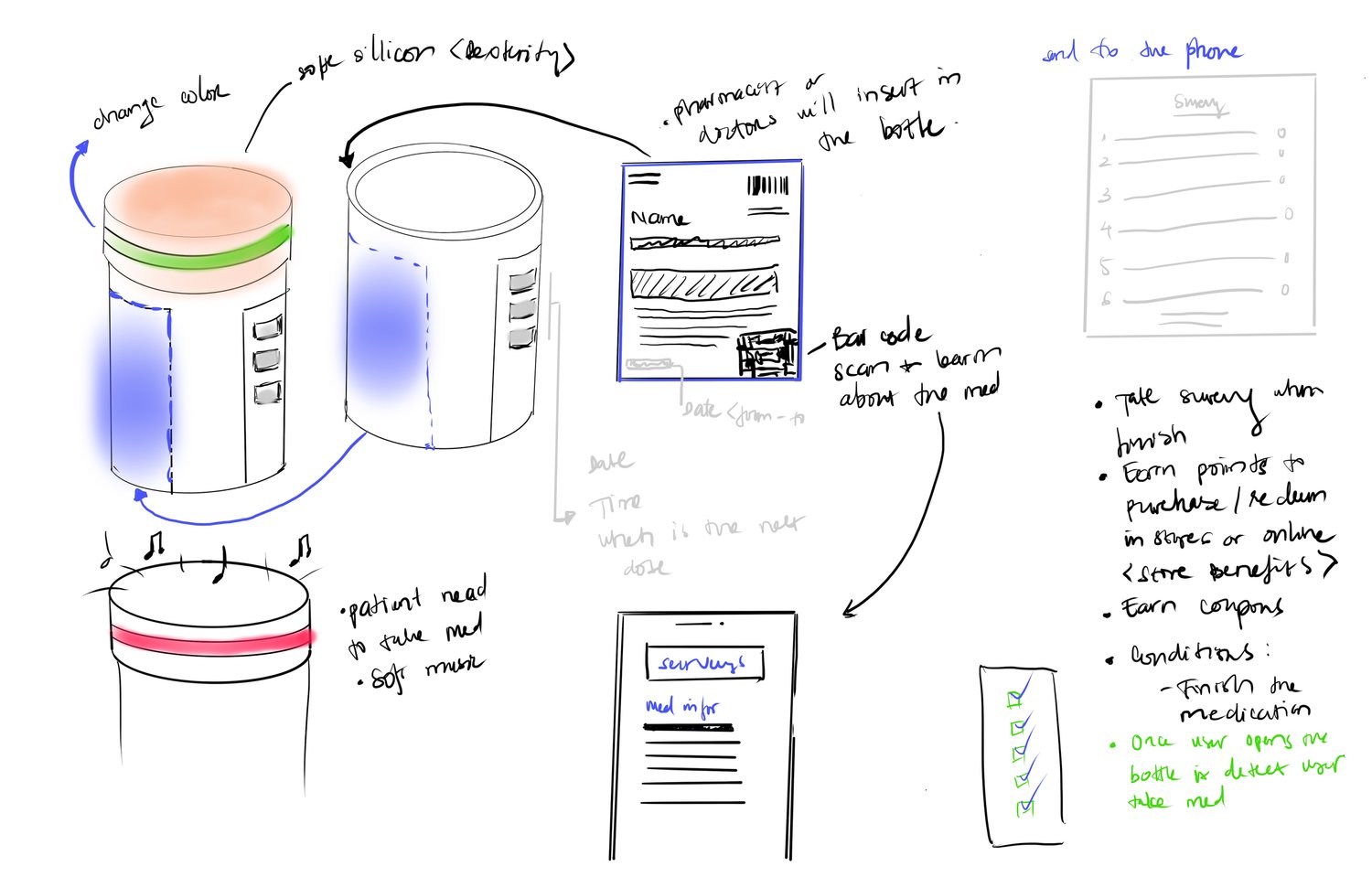
Concept Refinement
Digital Medicine Cabinet
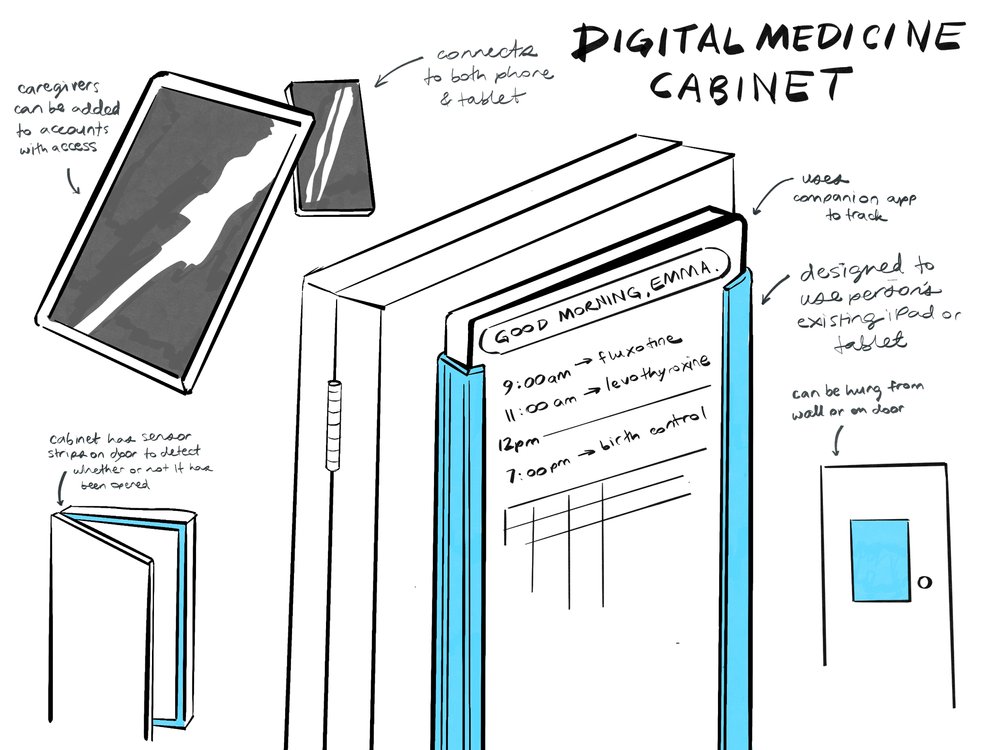
The digital medicine cabinet functions like a regular medicine cabinet for storage but adds connectivity to track cabinet openings, medication inventory, and refill scheduling through app integration.
Mobile Pill Carrier Evolution
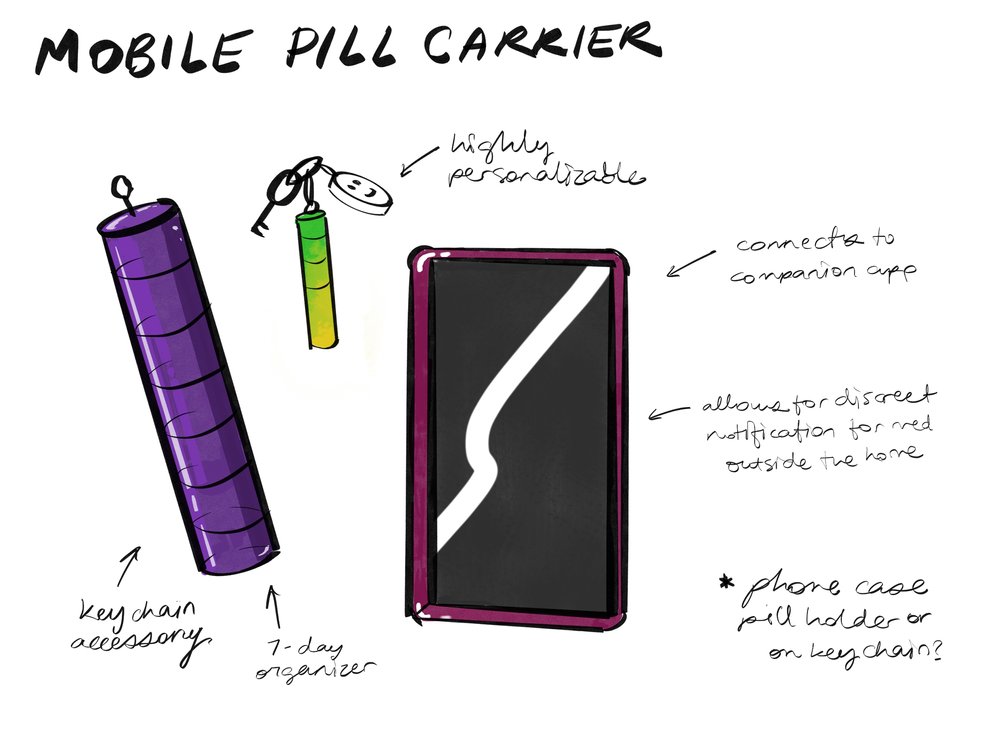
Initially conceived as a wearable watch, user research revealed resistance to replacing current wearables or adopting new ones. We evolved the concept into a keychain format—portable, discreet, personalizable, and always with the user.
Augmented Reality Integration
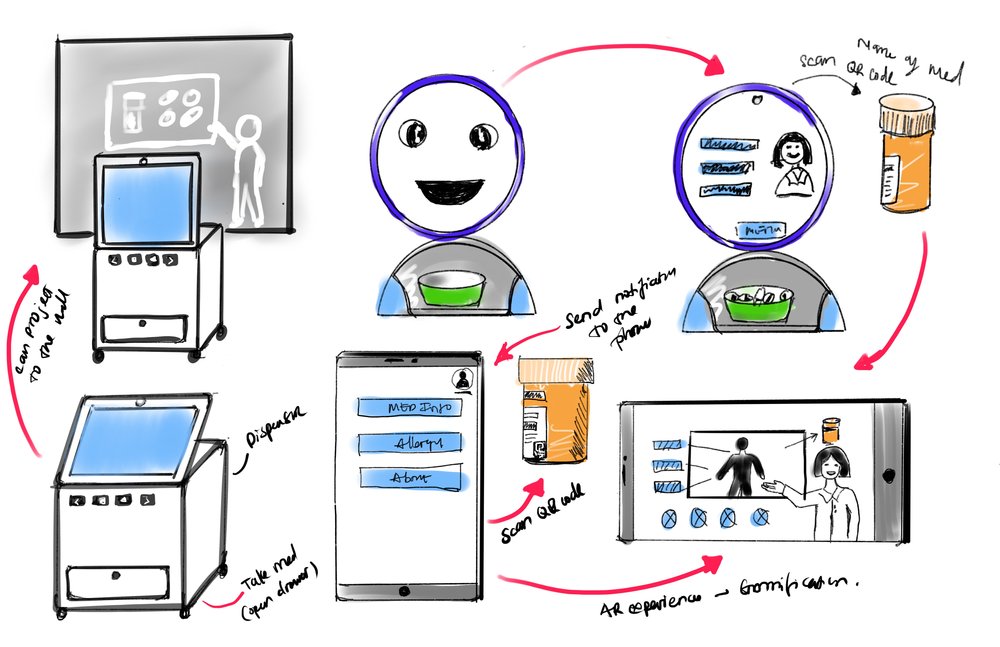
This concept integrated pill dispensers with AR experiences, allowing users to interact directly with devices to communicate with doctors and pharmacists while learning about medications. Built-in cameras could monitor medication taking and send notifications.
Final Concept: Tomo
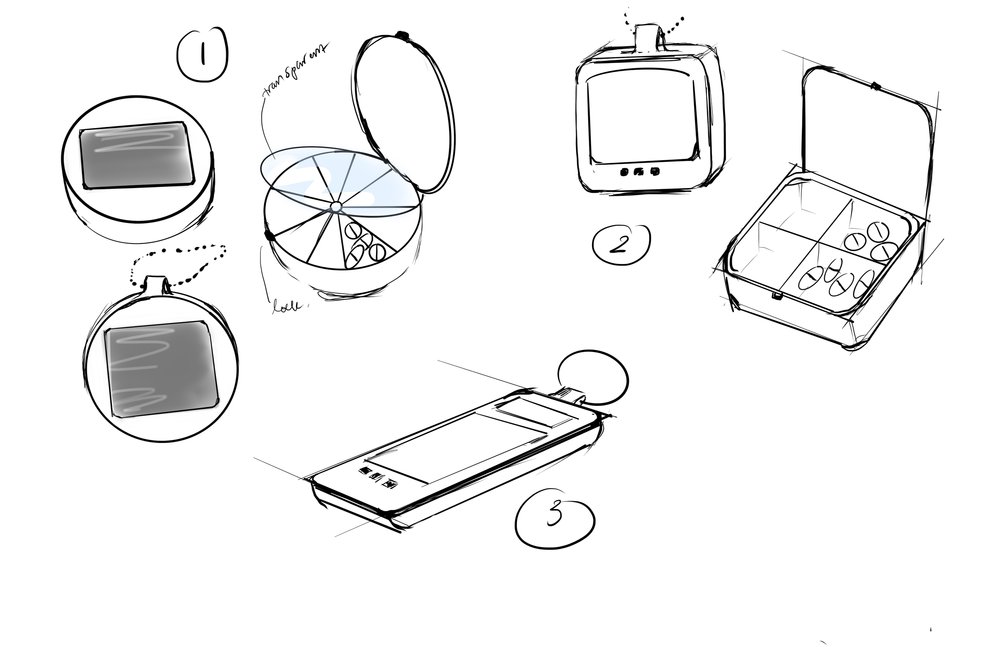
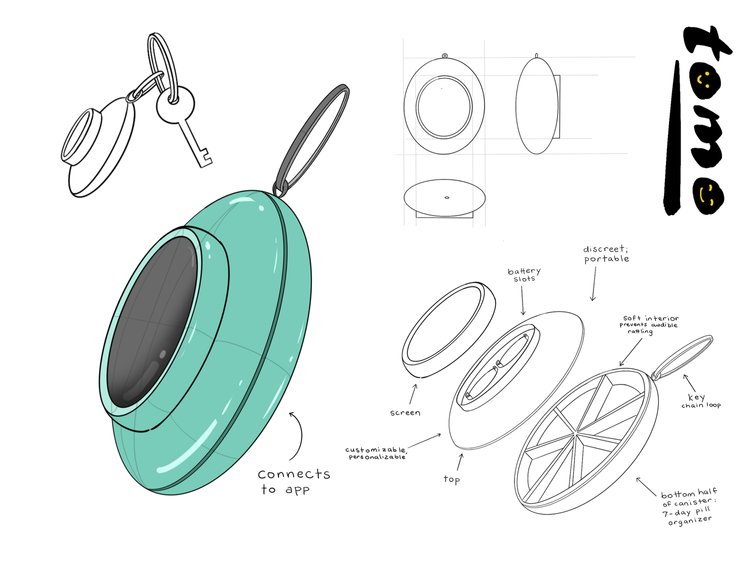
The concept for “Tomo” emerged as an uncomplicated solution prioritizing portability, discretion, and personalization. The design offers flexible functionality—education and community features within the paired app for users who want them, while also functioning as a basic reminder system for those needing simpler approaches.
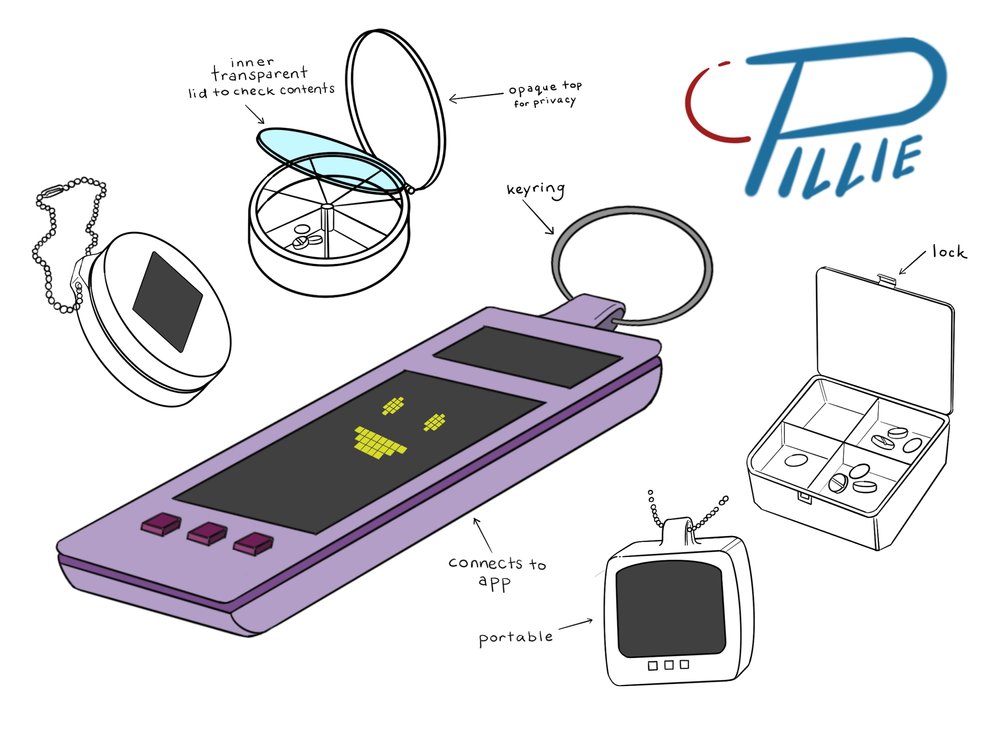
Alternative concepts like “Pillie” shared similar portability and personalization goals, designed as devices that help patients follow adherence protocols by managing medication and providing digital assistance for dose reminders.
User Experience Design & Prototyping
Future State Vision
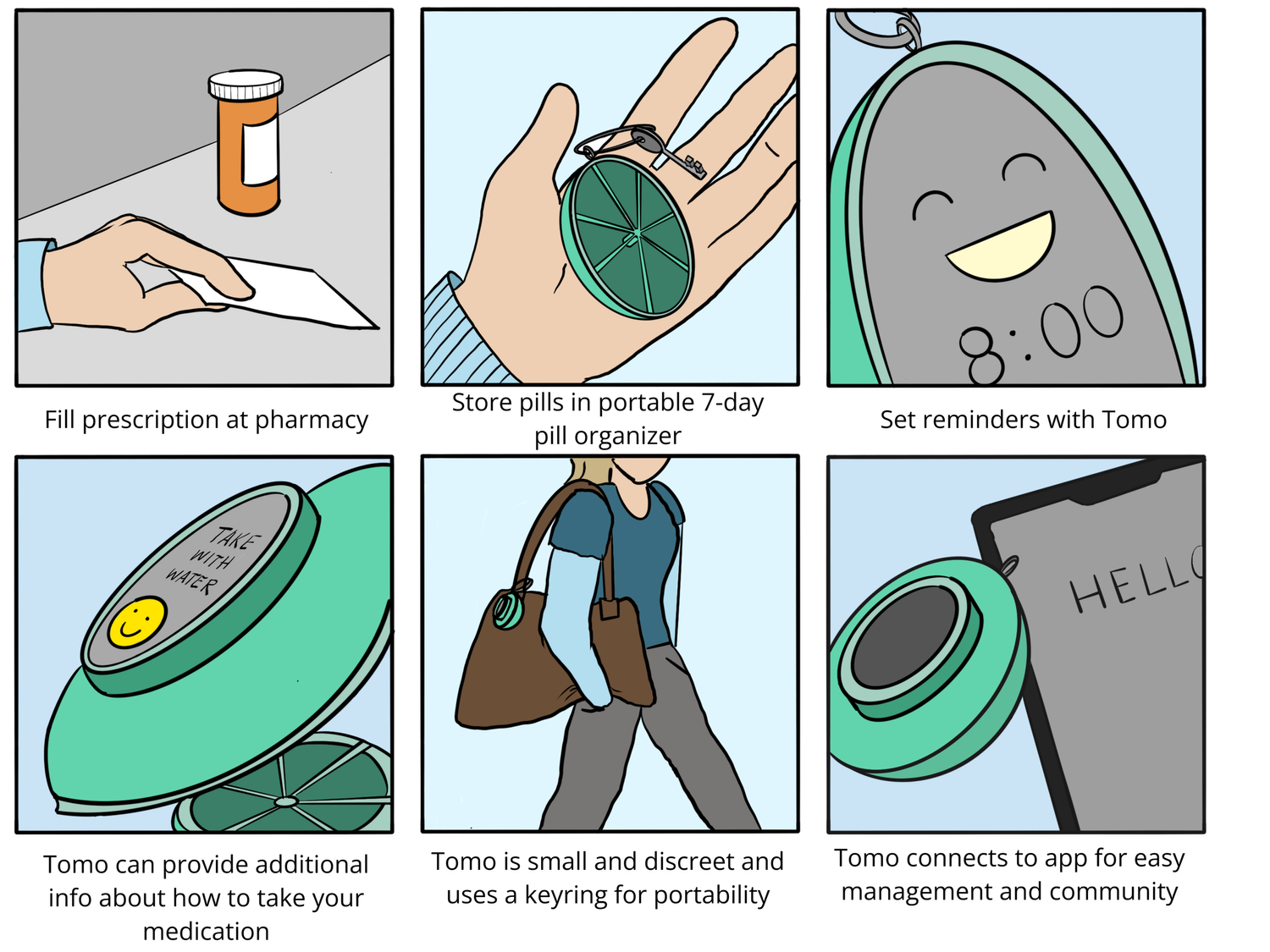
Our future state storyboard visualized how users might experience the medication journey when using Tomo, contrasting with the current state experience to highlight improvement opportunities.
User Flow Architecture
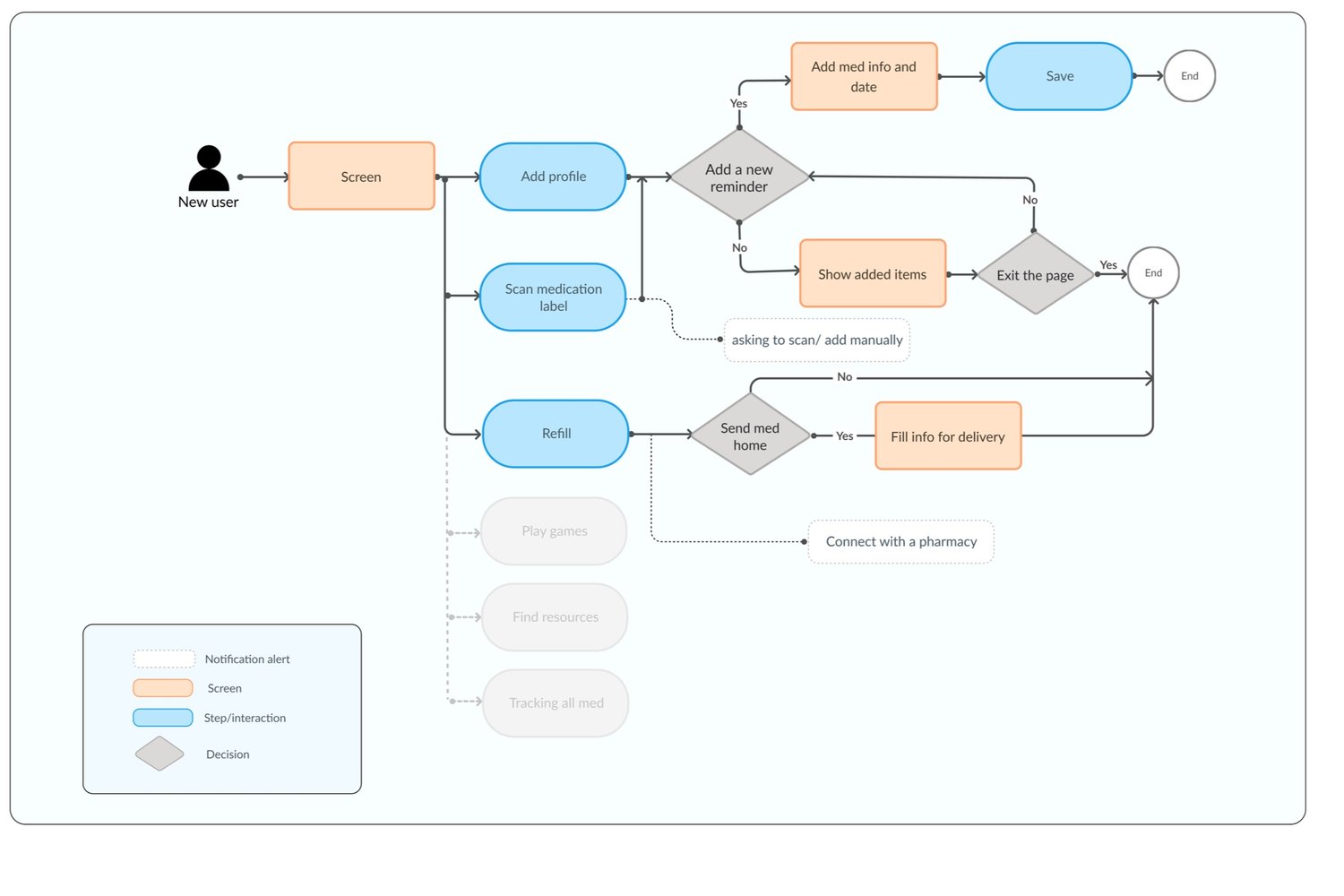
The user flow breaks down processes that occur when new users access the mobile application to add medication reminders or prescription refill alerts, ensuring intuitive onboarding and ongoing usage.
Task Flow Design
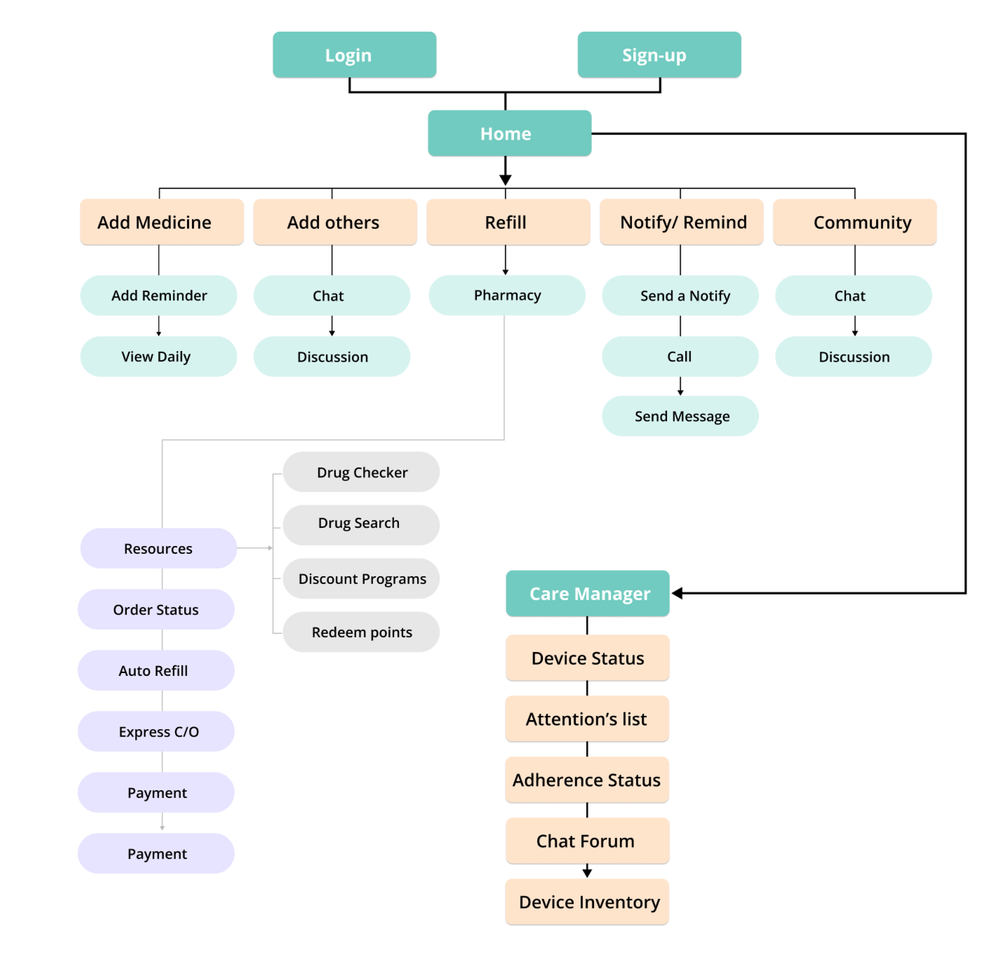
The task flow defines user journeys through specific tasks completed using the app, including adding medications and setting reminders, joining community discussions, and managing notifications for refills and appointments. This comprehensive mapping ensured all critical user paths were optimized for efficiency and clarity.
Low-Fidelity Prototyping
Digital-Physical Interface Integration

Users can choose different pets, known as “Tomos,” within the app, with changes appearing on the linked physical keychain. Users earn points toward Tomo upgrades and customization while personalizing profiles to join the community, share progress with caregivers, or maintain privacy.
Mobile Application Prototypes
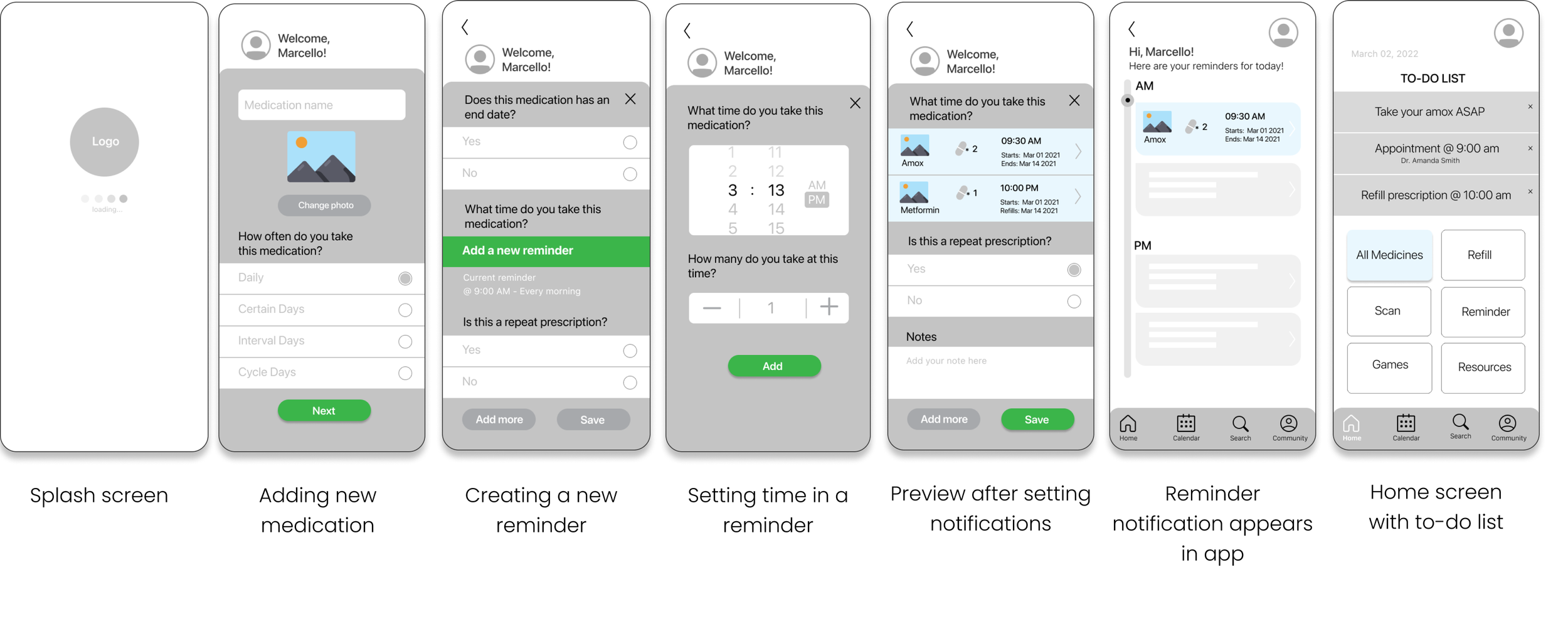
The low-fidelity prototypes show core application functionality including splash screens, reminder settings, and home screens featuring user to-do lists, community interfaces, friends lists, and adherence progress visualization.
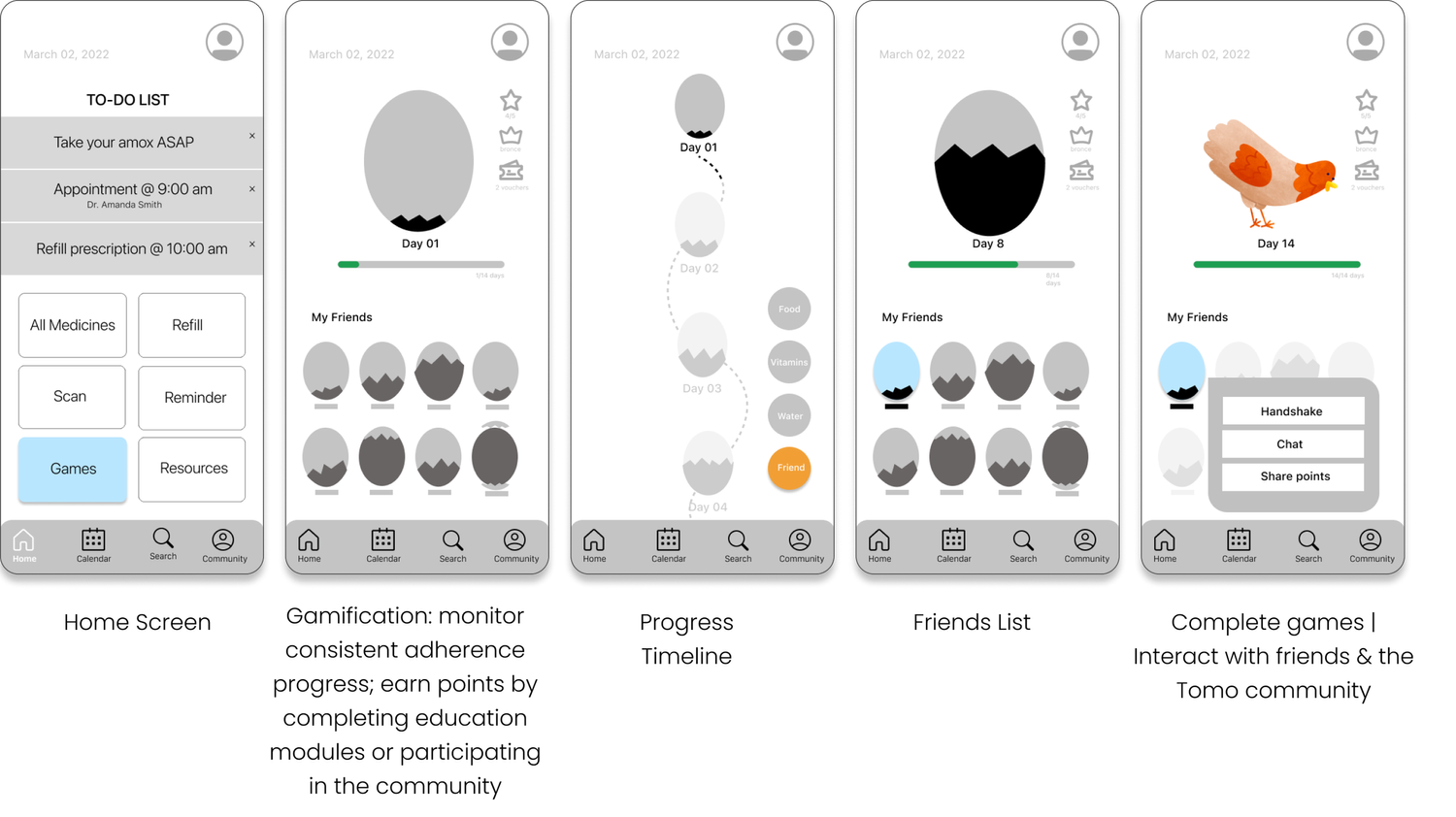
Community features enable peer support and shared experiences while maintaining user privacy controls and optional caregiver connections.
Low-Fidelity Physical Device Prototyping
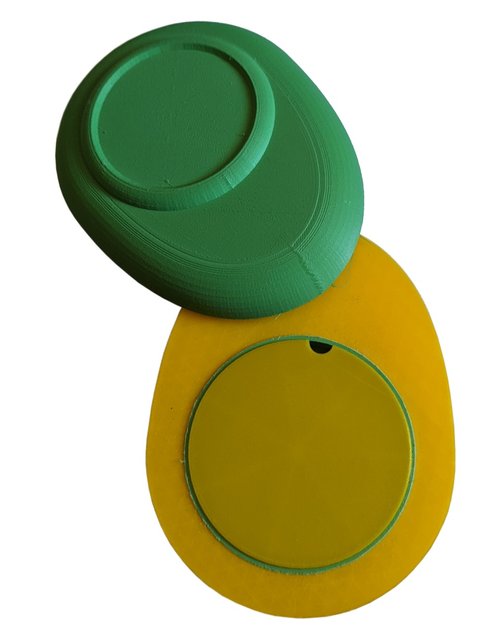
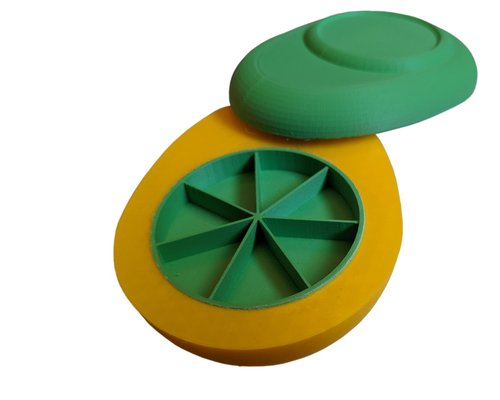
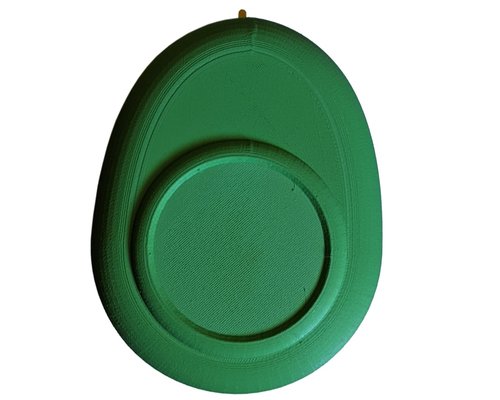


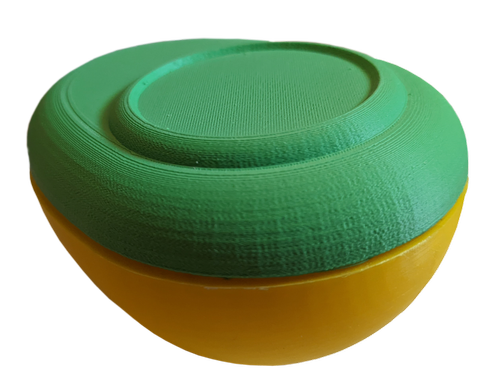

The physical device prototyping explored various form factors and interaction models. Early sketches and mockups helped us understand size constraints, user comfort, and technical feasibility before committing to the final keychain design.
High-Fidelity Prototyping & Visual Design
Brand Identity Development


Developing Tomo’s visual identity required balancing medical credibility with approachable, non-clinical aesthetics. The brand needed to feel supportive rather than intimidating, encouraging daily engagement without reinforcing illness identity.

Moodboard & Visual Direction

The visual design exploration balanced medical trustworthiness with wellness-focused approachability. Our moodboard guided color choices, typography, and imagery that would feel supportive rather than clinical, establishing the foundation for all subsequent design decisions.
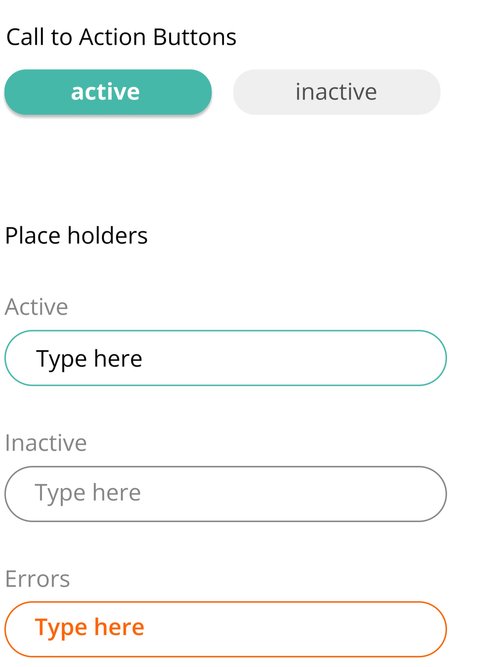
Visual Design Elements & System
![]()
The icon system reinforced Tomo’s friendly, approachable aesthetic while maintaining clarity across different device sizes and contexts. Each icon was designed to feel cohesive with the overall brand personality.
Mobile Application Design
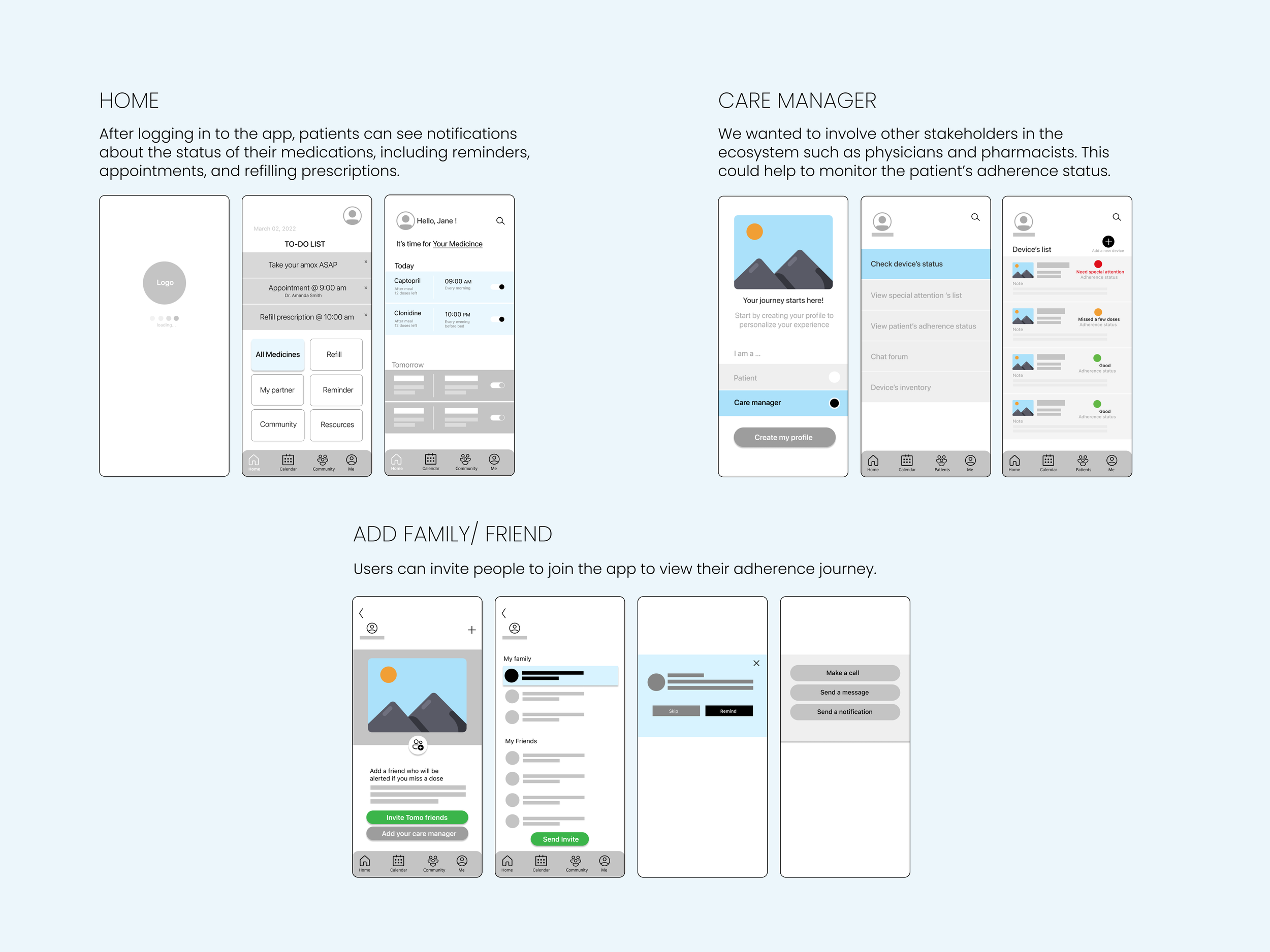
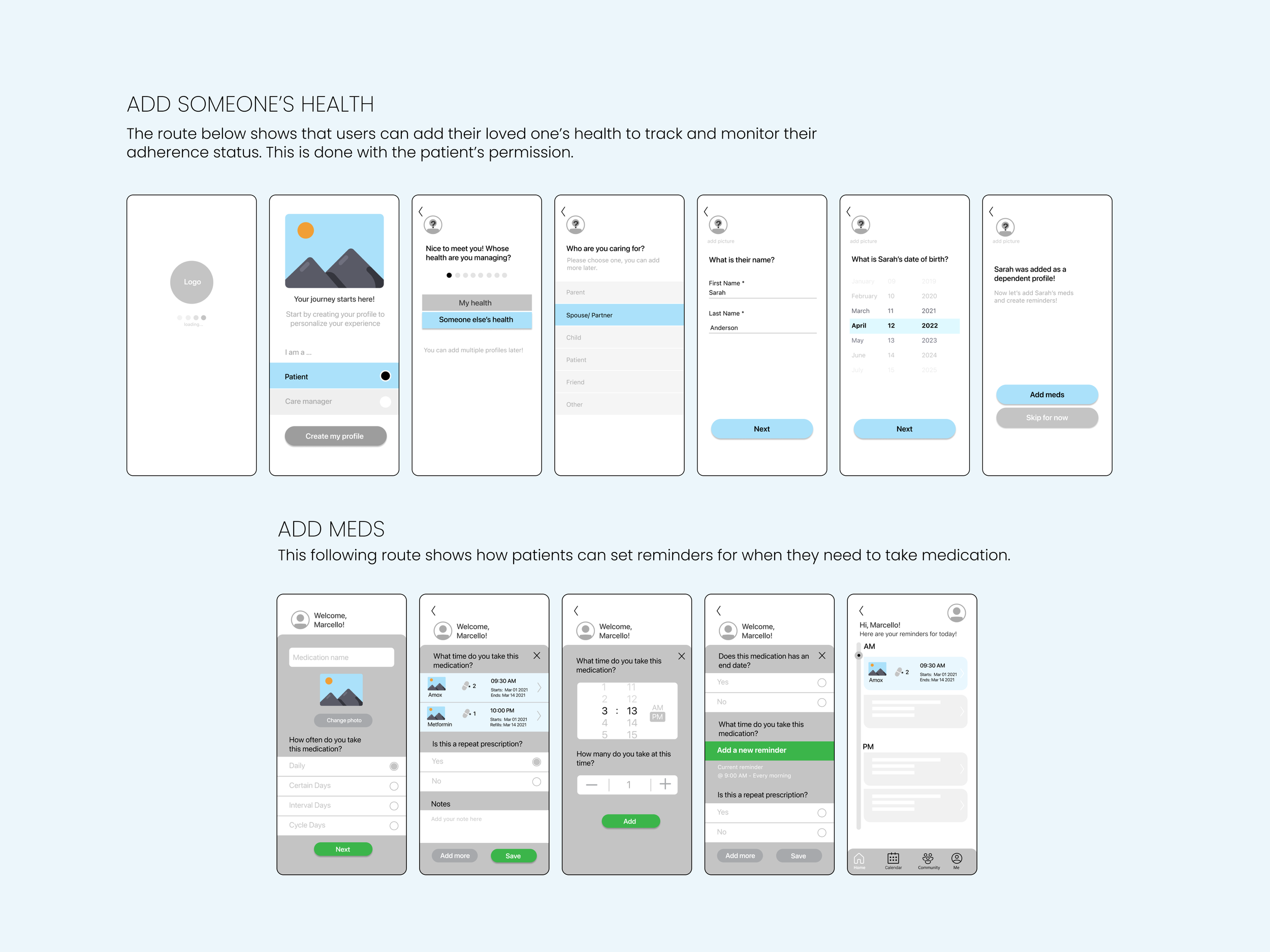
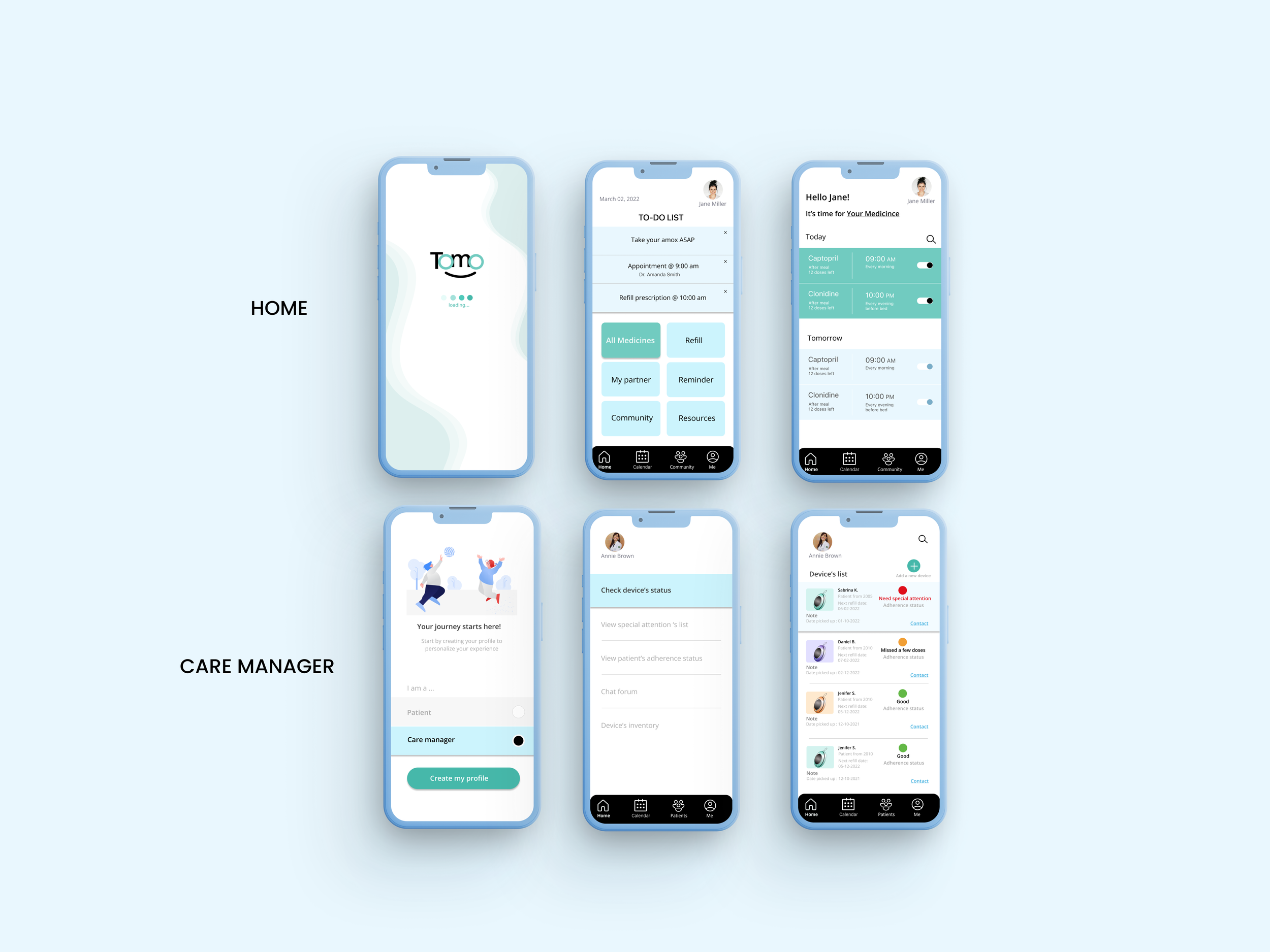
The high-fidelity prototype translated our research insights into polished interface design. Clean typography, intuitive navigation patterns, and gentle color schemes created an experience that felt more like a wellness app than medical software.
Physical Product Design Evolution
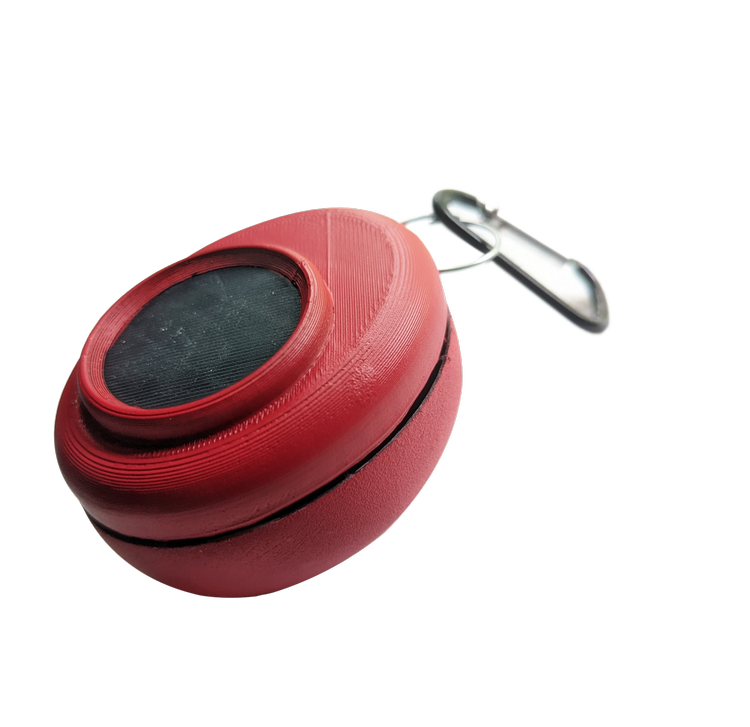
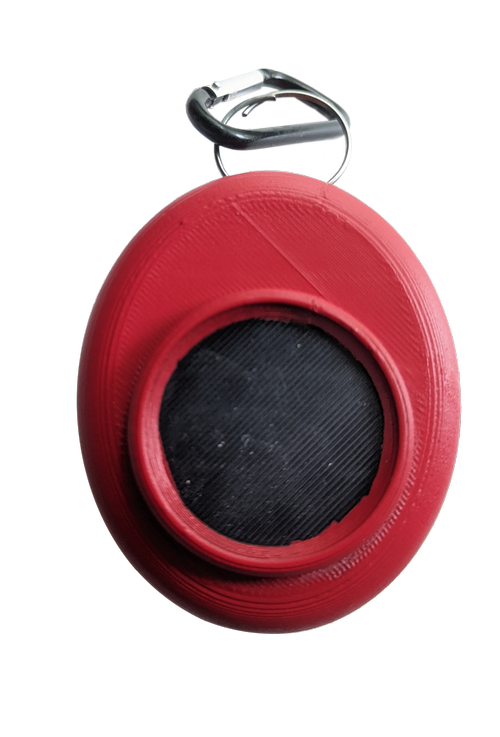


The physical Tomo device evolved through multiple iterations, balancing portability with functionality. The final keychain form factor emerged as the optimal solution—always accessible, customizable, and socially acceptable across different user contexts.
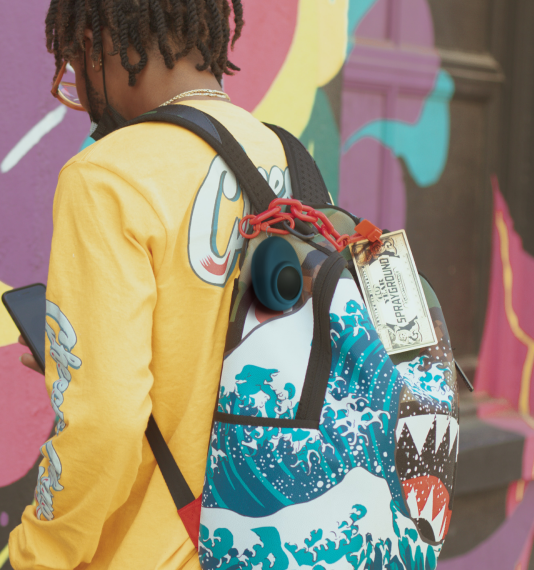

User Testing & Validation
Prototype Testing Process
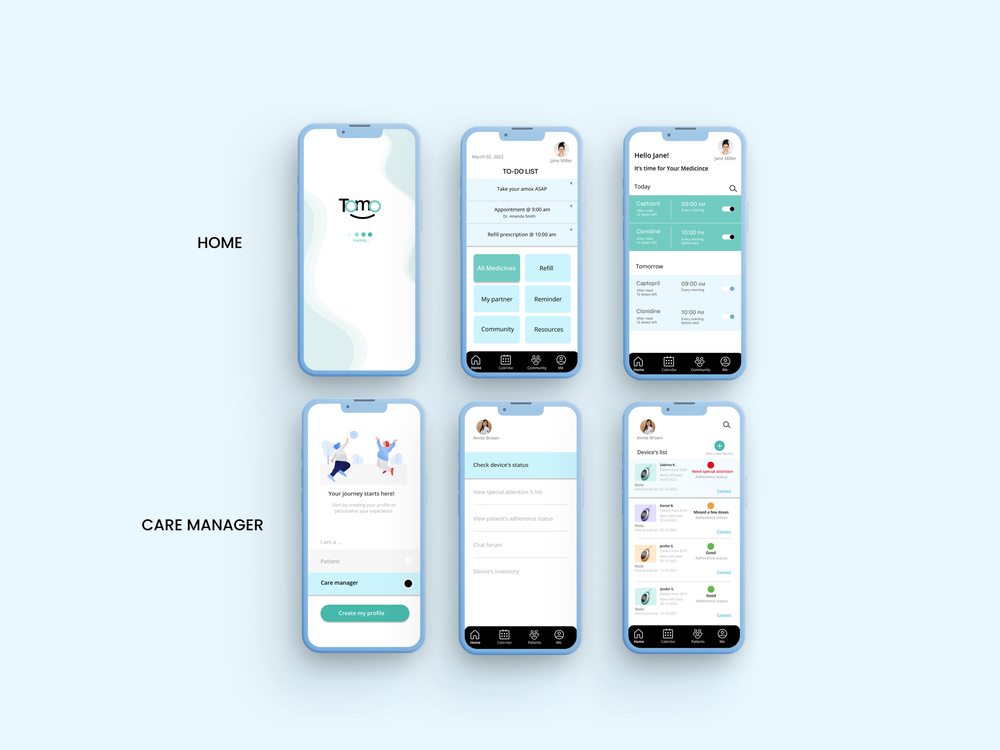
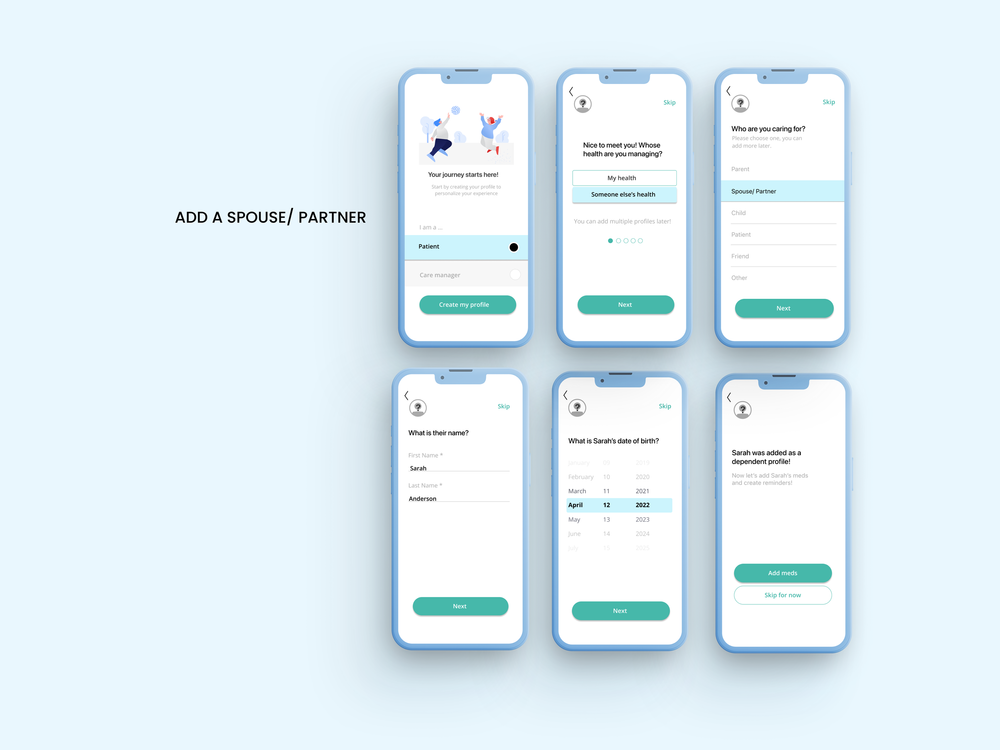
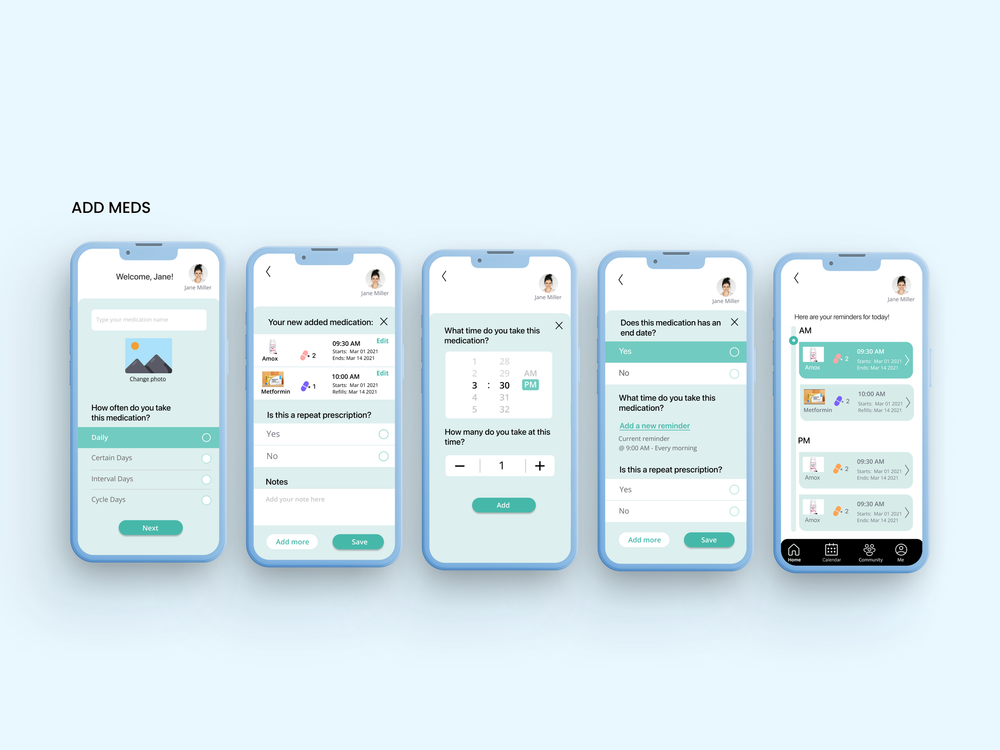
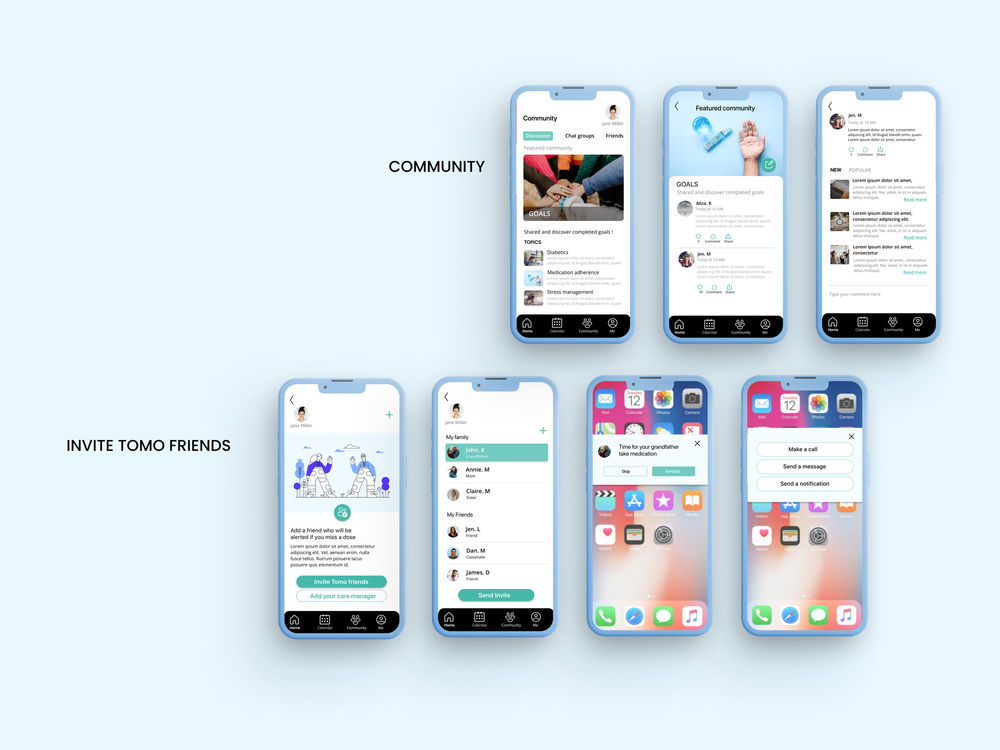
User testing validated our integrated approach, with participants responding positively to the dual digital-physical system. The combination addressed different failure modes—when digital reminders failed due to phone issues, the physical device provided backup, while the app’s intelligent features optimized timing when the device wasn’t immediately accessible.
Key Testing Insights
Testing revealed that users appreciated the flexibility to engage with different features based on their readiness and needs. Advanced users embraced community features and detailed tracking, while others preferred simple reminder functionality. This validated our layered approach to feature complexity.
The physical device testing showed strong adoption when users could customize appearance and functionality. The keychain format proved practical for daily carry, and the discrete design reduced social stigma concerns identified in our research.
Product Impact & Strategic Learning
Validated Design Approach
User research and prototyping validated that integrated digital-physical systems could improve adherence more effectively than either approach alone. The combination addresses different failure modes—when digital reminders fail due to phone issues, the physical device provides backup, while the app’s intelligent features optimize timing when the device isn’t immediately accessible.
Innovation in Healthcare Design
Tomo demonstrated that purpose-built adherence platforms could serve specific user needs more effectively than adapting existing tools. By focusing on behavioral support rather than just technological capability, the platform created value that mainstream digital solutions couldn’t provide.
The project validated that healthcare design challenges often require fundamental rethinking of existing paradigms rather than incremental improvements to current solutions, emphasizing human factors over purely technological approaches.
Strategic Business Implications
The dual-modality approach enables flexible pricing strategies and distribution partnerships. Healthcare providers can recommend the full system for complex cases while offering app-only options for less intensive needs, making the solution accessible across different economic segments and healthcare contexts.
Tomo exemplifies how strategic product design can tackle massive market problems by understanding the complex interplay of individual needs, system constraints, and business opportunities—creating solutions that deliver value across multiple stakeholder groups while remaining deeply user-centered.